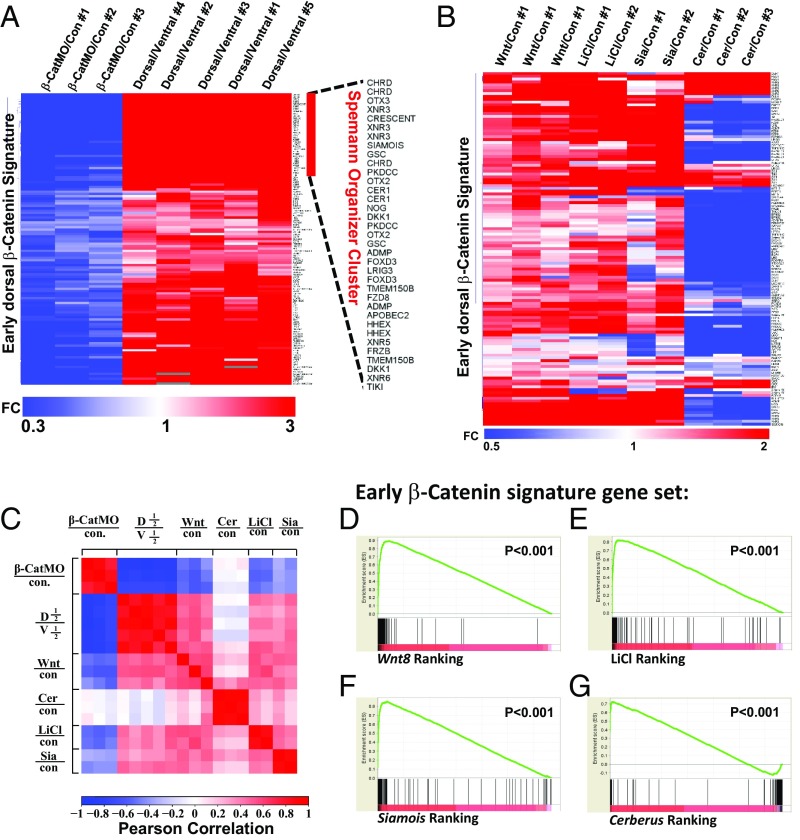
Fig. 4.
Correlation of the early dorsal β-catenin gene signature with Wnt8, LiCl, Siamois-induced genes, and Cerberus-repressed genes. (A) Heat map showing the fold change of early β-catenin signature genes in three β-catenin MO and five dorsal halves with respect to control and ventral half-embryo libraries, respectively. Fold changes (FC) over controls were used as inputs, and unsupervised hierarchical clustering of columns and rows was performed. Note that hierarchical clustering of rows identified most classic known Spemann organizer genes on the top of the heat map. (B) Heat map displaying regulation of genes composing the early β-catenin signature by Wnt8 mRNA, LiCl, and Siamois or Cerberus mRNAs. (C) Correlation matrix of β-CatMO–, Wnt8-, Cerberus-, and Siamois-injected embryos and LiCl-treated embryos with the early dorsal β-catenin signature. Correlation scores were calculated as Pearson correlation coefficients (PCCs) and were color-coded as shown in the scale bar on the bottom of the panel. Note that the β-CatMO (in blue) anticorrelates with all conditions except Cerberus mRNA-injected embryos. These results show that the early β-catenin signature obtained via RNA-seq is reproducible and readily identifies dorsalizing and ventralizing conditions. (D–G) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) showed that the early β-catenin gene set was significantly enriched at the top of the Wnt8-, LiCl-, and Siamois-induced gene rankings, and at the bottom of the Cerberus-induced ranking. Cer, Cerberus; con, control; D1/2, dorsal half; Sia, Siamois; V1/2, ventral half.