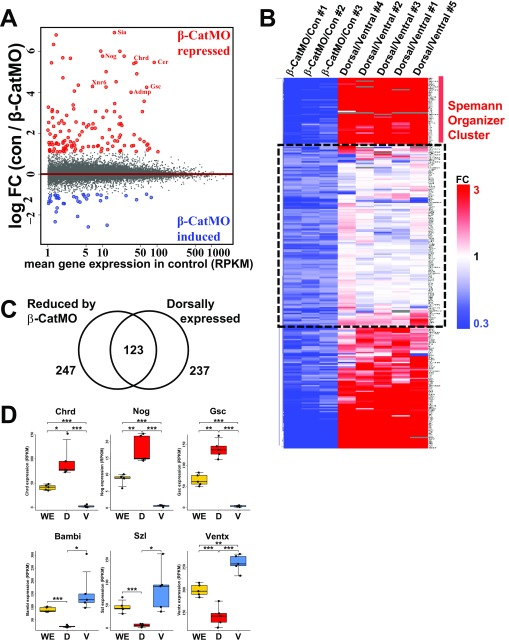
Fig. S1.
Transcriptome analysis of β-CatMO–injected embryos and dorsal and ventral halves. (A) MA-plot comparing gene expression between uninjected control and β-catenin MO–injected embryos including 16,729 transcripts. The average (three independent experiments) log2 fold change (FC) in expression of transcripts in control (con) embryos over β-CatMO–injected embryos (con/β-CatMO) is plotted on the ordinate; the average mean gene expression (in RPKM) in control embryos is represented on the abscissa. Red indicates β-CatMO–repressed transcripts (1.4-fold minimum decrease); blue indicates β-CatMO–induced transcripts (1.4-fold increased); gray dots indicate all other transcripts. Note that β-CatMO represses more genes than it activates, which is consistent with the widespread role of β-catenin as a transcriptional coactivator. (B) Heat map showing all transcripts that were repressed 1.4-fold by β-catenin MO in three independent pairs of libraries, and the dorsal to ventral (D/V) FC in five independent dorsal and ventral half libraries bisected at midblastula stage 8 and allowed to regenerate for 5 h until gastrula. Rows indicate FC of transcripts as indicated in the scale bar at the right of the panel. The various conditions are indicated at the top of the columns. Hierarchical clustering of rows clustered classical Spemann organizer genes on the top region. Genes within the dashed line box were repressed by β-CatMO but not enriched in the dorsal half; these were removed from our early β-catenin signature because they represent genes that require β-catenin independently of the maternal dorsal signal. (C) Venn diagram illustrating overlap of genes between β-CatMO–inhibited genes and dorsally enriched genes. Of 247 genes reduced by β-catenin MO and 237 genes enriched in dorsal side, 123 genes overlapped and defined our early dorsal β-catenin signature. In these stringent conditions, which require results above a certain threshold in all three independent experiments, some β-catenin–regulated genes may miss the cutoff. The complete stage 10.5 RPKM data are presented in Dataset S1, and, from this dataset, any genes that narrowly missed the cutoff can be retrieved. (D) Box plots of RPKMs of whole embryo (WE) and dorsal (D) and ventral (V) halves in five independent RNA-seq experiments. Note that, as expected, Chrd, Nog, and Gsc were significantly enriched in regenerating dorsal halves and that Bambi, Szl, and Ventx were enriched in ventral halves, which supports the quantitative nature of the RNA-seq analyses.