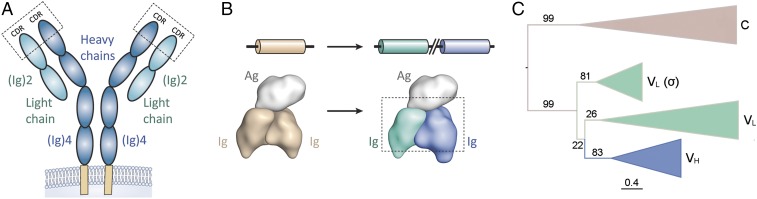
Fig. 1.
Evolution of rearranging Ig antigen receptors. (A) Chain structure of modern-day heterodimeric antigen receptors (IgG antibody isotype shown). The molecule is composed of two heavy chains (each containing four Ig domains, in blue) and two light chains (each containing two Ig domains, in cyan) (2). Hypervariable CDRs, which mediate contact with antigen, are highlighted. (B) Gene duplication and diversification events are believed to have converted a homodimeric Ig format (tan) to the heterodimeric format (cyan/blue) observed in the B lymphocyte-based (B-cell receptor, antibodies) and T lymphocyte-based (T-cell receptor) adaptive immune systems of jawed vertebrates. (C) Condensed maximum likelihood phylogeny of Ig heavy and light chains of vertebrates. Branches are labeled with bootstrap values from 100 replicates. (Scale bar: mean number of substitutions per site.) C, antibody constant.