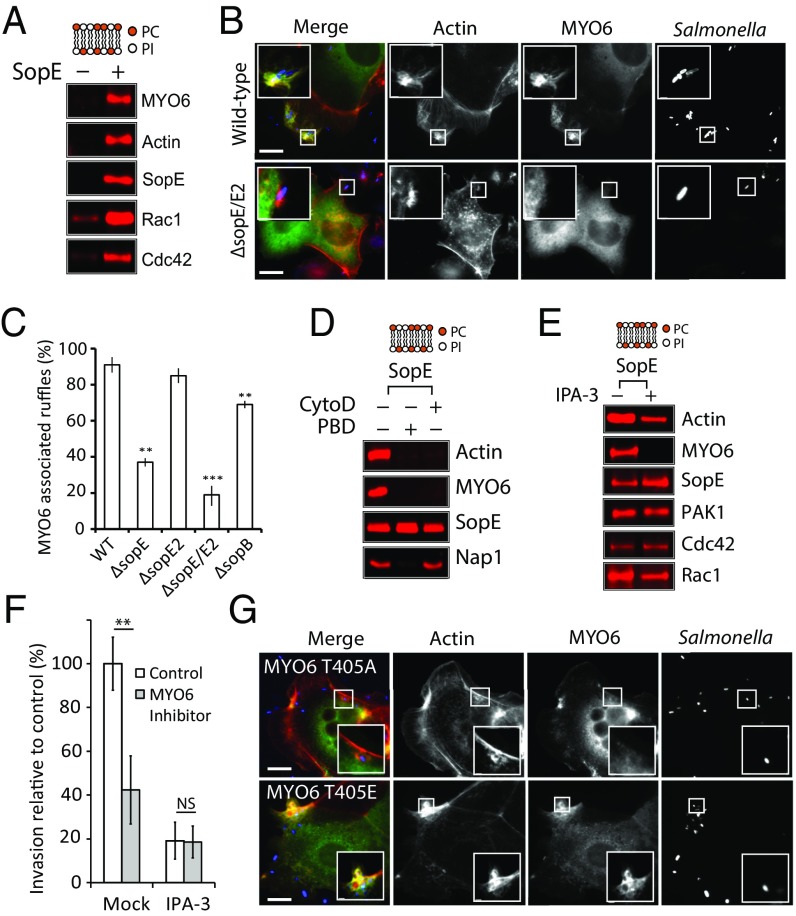
Fig. 2.
SopE manipulation of MYO6 and PAK. (A) PC:PI beads incubated in cell extract in the absence (−) or presence (+) of SopE were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Localization of GFP-MYO6 (green) in HeLa cells infected with wild-type or ΔsopE Salmonella. Bacteria were visualized using Salmonella antibodies (red) and actin filaments with Alexa-Fluor 350-conjugated phalloidin (blue). (Scale bars: 5 μm.) Insets 3× magnify Salmonella-induced ruffles. (C) Quantification of MYO6 localization to membrane ruffles. The experiment was performed as in B using wild-type, ΔsopE, ΔsopE2, ΔsopE/E2, and ΔsopB Salmonella. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (D) SopE recruitment of MYO6 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of inhibitors of actin polymerization (CytoD) and Rho GTPase signaling (PBD). The experiment was performed as in A. (E) SopE recruitment of MYO6 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the PAK inhibitor IPA-3. The experiment was performed as in A. (F) Salmonella invasion into HeLa cells in the absence (control) or presence of the MYO6 inhibitor TIP, with or without (Mock) the PAK inhibitor IPA-3 in combination. Error bars represent ± SEM; **P < 0.01. NS, nonsignificant. (G) Localization of GFP-MYO6 (T405A) or phosphomimic (T405E) to Salmonella-induced ruffles. The experiment was performed as in B. Insets 3× magnify Salmonella-induced ruffles. (Scale bars: 5 μm.)