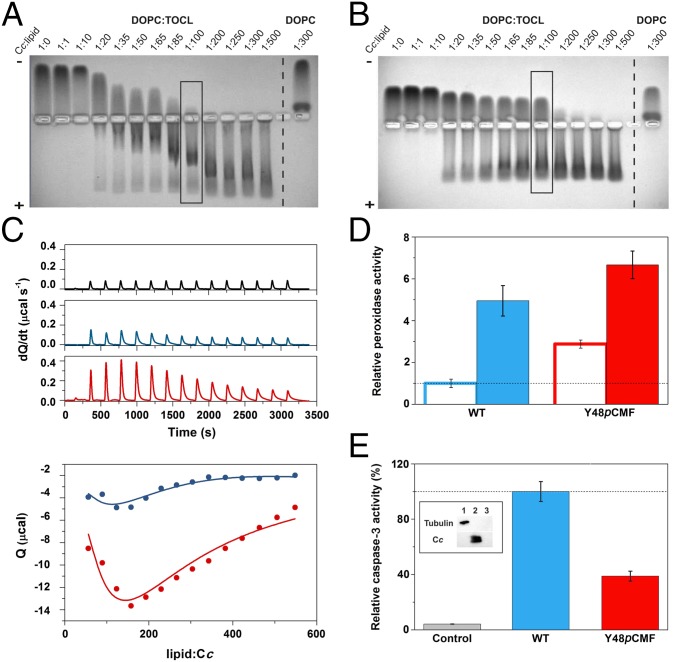
Fig. 6.
Liposome-binding assays with caspase-3 activity induced by WT and Y48pCMF Cc. (A and B) EMSA of Cc in the presence of increasing concentrations of lipids. DOPC:TOCL (4:1) or DOPC liposomes were incubated with WT (A) or Y48pCMF (B) Cc. Note that free Cc species moved to the cathode, whereas liposome-bound Cc migrated to the anode. Lanes marked by rectangles correspond to the Cc:lipid ratio at which the peroxidase activity was determined (see below). (C) Calorimetric assays for lipid binding to Cc. (C, Upper) ITC thermograms, corresponding to titrations of DOPC:TOCL 4:1 liposomes (black), WT Cc (blue), or Y48pCMF Cc (red). (C, Lower) Binding isotherms with WT Cc (blue dots) or Y48pCMF Cc (red dots). Continuous lines represent the best fits to a sequential binding, as computed with NanoAnalyze software (TA Instruments) with a stoichiometry of 30 molecules of lipid per molecule of Cc. All data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (D) Relative peroxidase activities of WT Cc (blue) or Y48pCMF Cc (red) in the presence of liposomes containing DOPC (empty bars) or DOPC:TOCL (4:1) (filled bars). (E) Relative caspase-3 activity in HEK293 cell extracts devoid of endogenous Cc upon addition of exogenous WT Cc (blue) or Y48pCMF Cc (red). A lack of caspase autoactivation was verified in a run without the addition of Cc (gray). Western blots confirmed the lack of endogenous Cc in cytoplasmic cell extracts after immunoblotting with anti–α-tubulin (cytosolic marker) and anti-Cc antibodies (Inset). Lane 1, cytoplasmic cell extracts; lane 2, Cc; lane 3, BSA as a negative control. All data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.