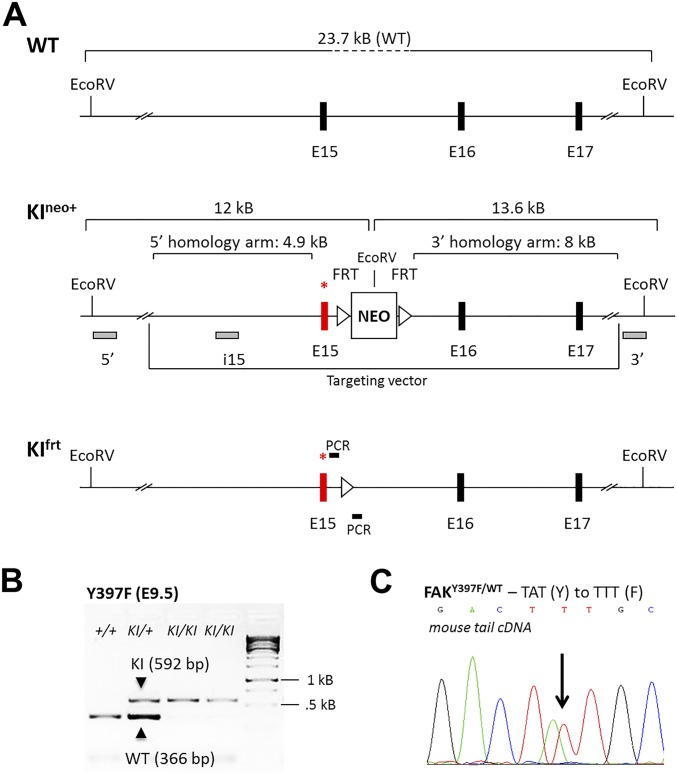
Fig. S1.
Generation of FAKY397F knock-in (KI) mice. (A) Partial map of the FAK allele. Exon 15 (E15), which contains mutated Y397, is marked by an asterisk, before (KIneo+) and after (KIfrt) flippase-mediated deletion of the flirted (FRT) neocassette. The DNA fragment sizes obtained after EcoRV restriction digest, as well as probes (5′ and 3′ probes external to the targeting vector and the i15 internal probe) used for Southern blotting are shown. Filled boxes indicate exons, and triangles indicate FRT sites. Location of PCR primers for KIfrt mice genotyping is depicted: forward, GCTTTAGAGCACATCTGTCAC; reverse, CTGGGCTGCTTGAATAGTGGG. NEO, neomycin resistance gene; WT, wild-type. (B) Representative PCR genotyping of KIfrt embryos at E9.5 using primers flanking the FRT site. The expected PCR product size is 592 bp for the KI allele and 366 bp for the WT allele. PCR results from WT embryos (+/+), heterozygous embryos (KI/+) and homozygous embryos (KI/KI) are shown for both of the Y397F KIs. kB, kilobase. (C) Sanger sequencing of cDNA derived from the tails of heterozygous KI mice. Double peaks are indicative of base pair changes in the respective KI alleles. Y, tyrosine codon sequence; F, phenylalanine codon sequence.