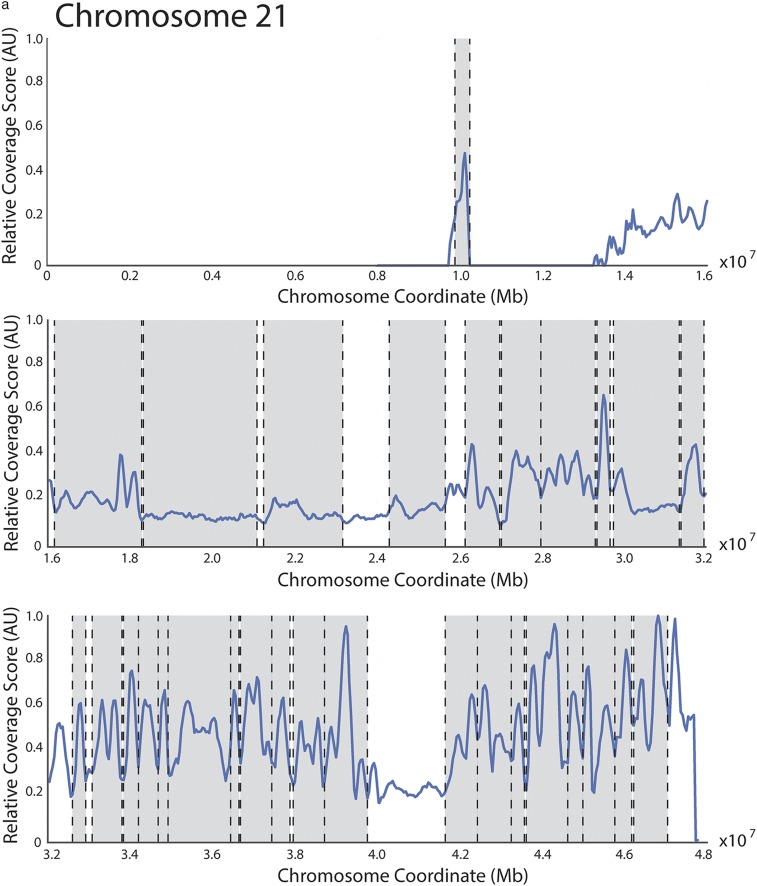
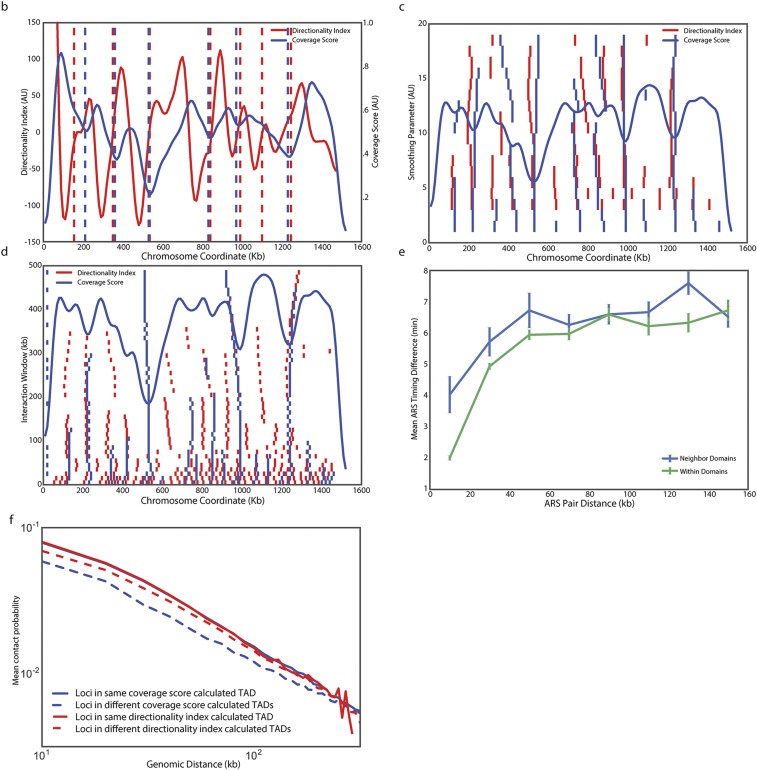
Fig. S1.
Coverage score identifies domain boundaries that are similar to but not identical to the boundaries found using the directionality index. (A) Hi-C data from human IMR90 fibroblasts from Dixon et al. (8) was analyzed as the yeast Hi-C data to produce a coverage score across chromosome 21. No parameters were modified from the yeast analysis. This finding indicates that coverage score minima frequently correspond to domain boundaries previously identified using a hidden Markov model (8). Previously identified domains are denoted with shaded regions and boundaries by dashed lines. (B) Plot comparing budding yeast chromosome IV coverage score (blue) to the directionality index defined by Dixon et al. (8) (red). Boundaries identified by each metric are shown with color matched dashed vertical lines. Boundaries for the directionality index were identified as locations where the smoothed directionality score transitioned from negative to positive values. Plots of boundaries identified on yeast chromosome IV using the directionality index and coverage score methods when parameters are varied. When either the smoothing parameter (C) or the interaction window (D) are varied, the number and positions of boundaries change less for coverage than for directionality. In C and D, coverage score is plotted (blue curve) for comparison. The y axis denotes the value of the parameter being varied. Small vertical tick marks denote boundaries found using either coverage score (blue) or directionality index (red). (E) The difference in replication timing for pairs of replication origins located within the same domain (green) or across domain boundaries (blue) is more similar when boundaries are identified using the directionality index than when boundaries are identified using the coverage score (smoothing parameter = 10, interaction window = 50 kb for both methods) (compare with Fig. 4C). (F) Normalized interaction frequency plotted as a function of distance for pairs of loci located within domains (solid) or across domain boundaries (dashed) calculated using the coverage score (blue) or directionality index (red) metrics. The effect of coverage score calculated domain boundaries on interaction frequency is more pronounced.