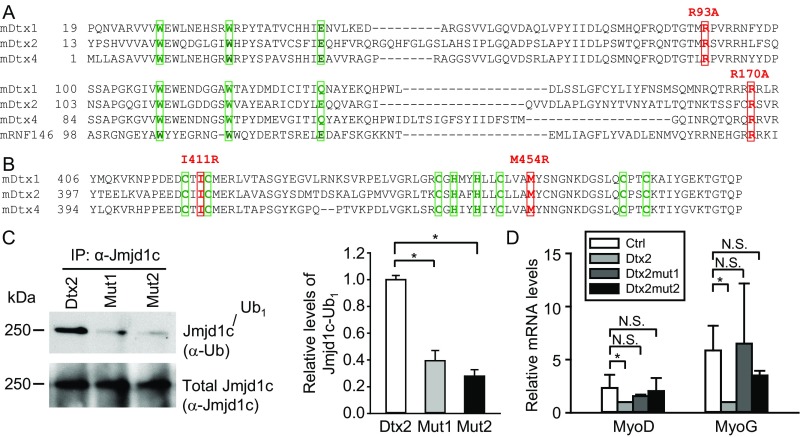
Fig. S8.
Multiple sequence alignment of WWE and RING domains in mouse Deltex family members. (A) Mouse Deltex family proteins and RNF146 protein sequences in WWE domains were aligned by a protein sequence alignment program, Clustal Omega (86). The three most conserved amino acid residues in two WWE domains are shown in green boxes. Two amino acid residues, R93 and R170, which are key residues for the binding of the WWE domains to PAR, are highlighted in red boxes. In Mut1, each residue was mutated to disrupt the binding of Deltex2 to PAR. (B) Alignment of protein sequences in RING domains of mouse Deltex family proteins. The key residues to form Zn fingers in the Deltex family RING domains are shown in green boxes. Two amino acid residues, I411 and M454, which are key residues for the interaction of RING domains with E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, are shown in red boxes. In Mut2, each residue is mutated to R to disrupt the interaction of Deltex2 with its E2 enzyme. (C) Analysis of the levels of Jmjd1c monoubiquitination. (Left) C2C12 myoblasts were transfected with Deltex2 (Dtx2), mutant Deltex2 R93A-R170A (Mut1), or mutant Deltex2 I411R-M454R (Mut2) expression constructs and lysed. Monoubiquitinated Jmjd1c was detected with an anti-ubiquitin antibody (FK2), and total Jmjd1c protein (native and monoubiquitinated) was assessed with an anti-Jmjd1c antibody. (Right) Quantitative analysis of the monoubiquitinated Jmjd1c. n = 3. (D) WT recombinant Deltex2 or two independent activate site mutants were expressed in primary differentiating myoblasts, and MyoD and MyoG mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05; N.S., not significant.