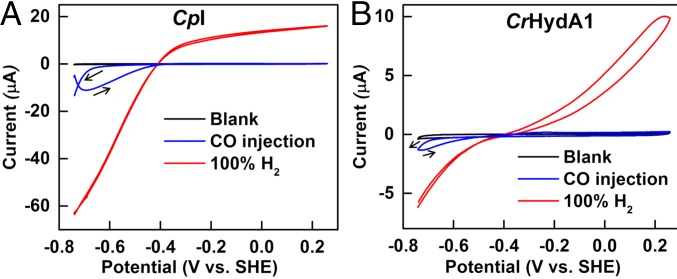
Fig. 2.
Cyclic voltammetry profiles of [FeFe]-hydrogenases, CpI (A) and CrHydA1 (B), on PGE electrodes and equilibrated with 100% H2 flowing in the headspace (red trace): the trace shows that, depending upon the potential applied, both H2 oxidation and H+ reduction are carried out by the enzyme. When CO is injected, the enzymes are unable to carry out H2 oxidation, and H+ reduction begins at a more negative potential (below −0.6 V vs. SHE) where CO is released (blue trace). Conditions: pH 7.0 (0.10 M phosphate buffer); temperature, 0 °C; scan rate, 20 mV⋅s−1.