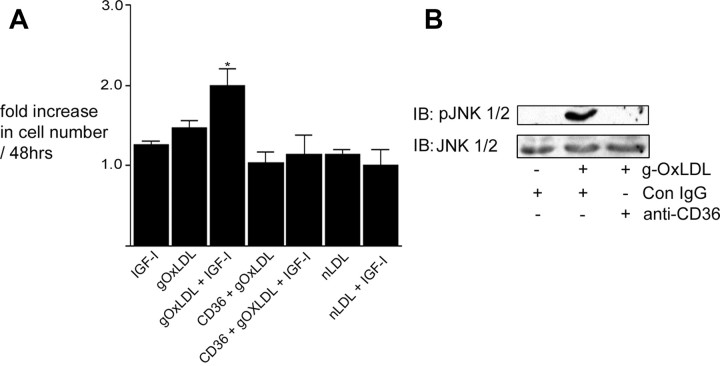
Fig. 1.
g-OxLDL increases IGF-I-stimulated SMC proliferation in a CD36-dependent manner. A, Cells (2 × 104) were plated in each well of a 24-well plate before exposure to IGF-I (50 ng/ml), g-OxLDL in the presence of control antiserum (5 μg/ml), n-LDL (5 μg/ml), or g-OxLDL in the presence of the anti-CD36 (CD36) antiserum (all prepared in DMEM plus 0.2% platelet poor plasma). At 48 h after the addition of IGF-I (50 ng/ml), cell number was determined by trypan blue staining and counting. *, P < 0.05 when cell number in response to IGF-I in the presence of g-OxLDL is compared with the number of cells in the presence of IGF-I alone. B, SMC were grown to confluency in medium containing 5 mm glucose before overnight incubation in SFM. g-OxLDL (5 μg/ml) was added for 4 h. Where indicated, either control IgG or anti-CD36 antiserum was added for 30 min before the addition of the LDL preparation. Phosphorylation of JNK was determined by immunoblotting (IB) equal amounts of cell lysates with an antibody specific for the phosphorylated form (pJNK). To demonstrate that there as no significant difference in the amount of total protein, blots were reprobed with an antibody that recognizes total JNK protein.