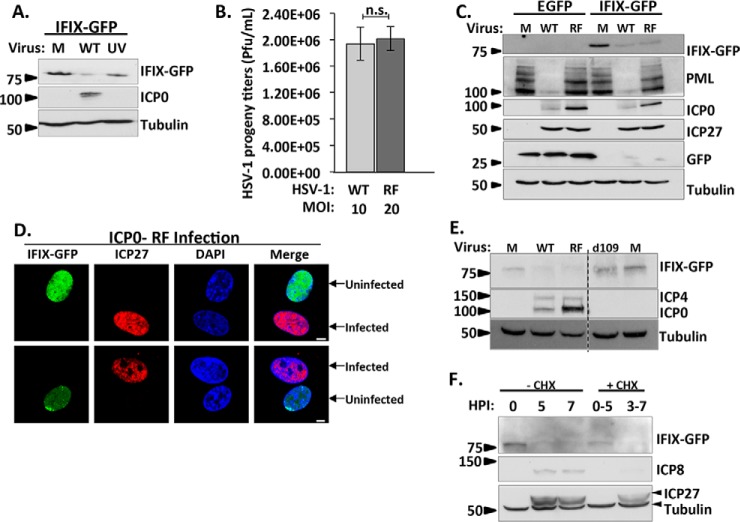
Fig. 5.
Decrease in IFIX levels requires viral gene expression, yet is not dependent on the E3 ligase activity of the viral protein ICP0. A, UV-induced inactivation of viral genes rescues IFIX protein levels. Cells were mock-infected (M) or infected with WT or UV-treated HSV-1 at m.o.i. 10, harvested at 6 hpi, and analyzed by Western blotting. B, testing equivalence of infection progression of wild type HSV-1 and ICP0 RING finger mutant (RF) HSV-1 by comparing HSV-1 progeny titers in HFF cells stably expressing EGFP. Cells were infected with WT at m.o.i. 10 or RF at m.o.i. 20. Cells and supernatants were collected at 22 hpi (95% cytopathic effect) and titered on U2OS cells. n.s., not significant. Error bars represent S.D. of two biological replicates run in technical duplicates. C, Western blot in HFFs stably expressing EGFP or IFIX-GFP comparing the indicated proteins during mock, WT (m.o.i. 10), or RF (m.o.i. 20) infection was at 6 hpi. IFIX levels decrease during infection with WT and RF viruses. PML is blotted to show ICP0 ligase activity is inhibited in the RF virus. ICP0 is marker for infection; ICP27 displays equal levels in both viruses. D, microscopy during RF infection displays decrease in IFIX-GFP in primary fibroblasts stably expressing IFIX-GFP. m.o.i.: 3, 6hpi; ICP27 is marker of infection. Bar, 5 μm. E, Western blot in HFFs stably expressing IFIX-GFP demonstrate IFIX levels do not decrease during d109 virus infection. Mock (M), WT (m.o.i. 10), RF (m.o.i. 20), or d109 (m.o.i. 20) infection was at 6 hpi. ICP4 and ICP0 are markers for infection and a validation for d109, which lacks all immediate-early genes. F, time course analyzed by Western blotting comparing IFIX-GFP levels in fibroblasts treated with cycloheximide (CHX) at 10 μg/ml to inhibit immediate-early viral protein expression (0–5 hpi) or delayed-early viral protein expression (3–7 hpi) and IFIX-GFP levels in fibroblasts not treated with CHX during WT HSV-1 infection.