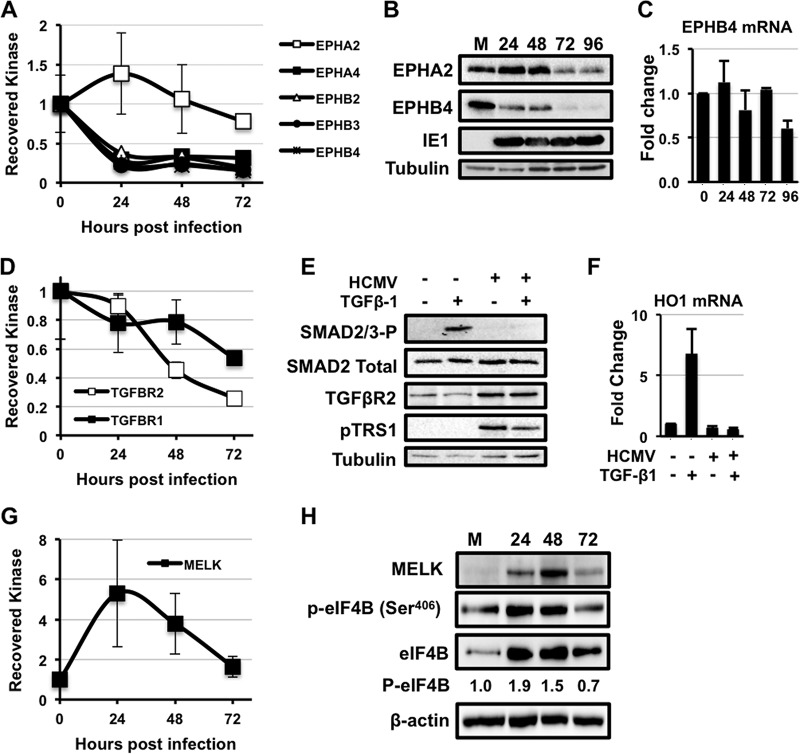
Fig. 3.
HCMV infection alters multiple novel signaling pathways. A, Fold change in the amount of ephrin (Eph) kinases recovered with MIBs over a time course of HCMV infection relative to uninfected cells. Primary human fibroblasts were infected with either AD169 or TB40E as in Fig. 1. The results are the average from all infections combined. B, MRC-5s were serum-starved for 24 h before infection with AD169 at a multiplicity of three. The levels of the Ephrin A2 (EPHA2), Ephrin B4 (EPHB4), and IE1 proteins were measured by Western blot over a time course of infection. The levels of tubulin were measured as a loading control. C, As in (B), levels of EphB4 mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR. D, Same as in (A). E, MRC-5s were infected with AD169 at a MOI of 3 for 48 h. Cells were then treated with 4 μg of TGF-β1 for 4 h. Levels of Smad2/3-P, Smad2, TGF-β receptor II, and pTRS1 were determined by Western blot. F, MRC-5s were infected as in (D). Cells were then treated with 4 μg of TGF-β1 for 24 h. Levels of HO1 mRNA (a Smad2/3-responsive transcript) were measured by qRT-PCR. G, Fold change in MELK kinase as in A. H, H, Western blot for MELK expression, eIF4B Ser406, total eIF4B and actin expression as in B. I, Western blot results for phosphorylation of the MELK substrate eIF4B (Ser406) and total eIF4B.