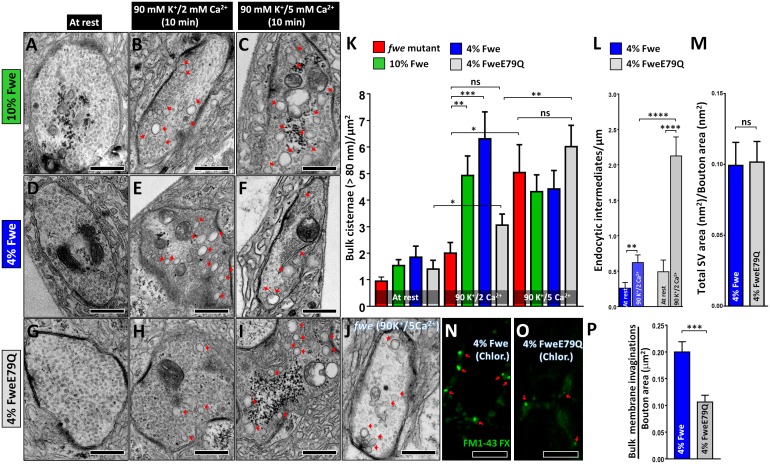
Fig 4. Ca2+ influx mediated by Fwe initiates Activity-Dependent Bulk Endocytosis (ADBE).
(A–J) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of neuromuscular junction (NMJ) boutons were obtained from larvae of the indicated genotypes. Samples were fixed under the resting condition (10-min incubation in 5 mM K+/0 mM Ca2+ solution, A, D, and G), after 10-min 90 mM K+/2 mM Ca2+ stimulation (B, E, and H), or after 10-min 90 mM K+/5 mM Ca2+ stimulation (C, F, I, and J). Bulk cisternae larger than 80 nm are indicated by red arrows. (K) Data quantifications of the number of bulk cisternae per bouton area. The data for fwe mutants at rest and after 90 mM K+/2 Ca2+ stimulation are derived from Fig 2G. Stimulation with 90 mM K+/5 mM Ca2+ solution induces a wild-type level of bulk cisternae in 4% FweE79Q-rescued and fwe mutant boutons. Type Ib boutons (at rest: fwe mutant, n = 31; 10% Fwe, n = 17; 4% Fwe, n = 21; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 12. Ten-minute 90 mM K+/2 mM Ca2+ stimulation: fwe mutant, n = 22; 10% Fwe, n = 27; 4% Fwe, n = 23; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 26. Ten-minute 90 mM K+/5 mM Ca2+ stimulation: fwe mutant, n = 23; 10% Fwe, n = 30; 4% Fwe, n = 24; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 27) derived from ≥3 larvae for each genotype were analyzed. (L) Data quantifications of the number of endocytic intermediates per periactive zone length. Following high K+ stimulation, more endocytic intermediates were found in 4% FweE79Q-rescued boutons when compared to 4% Fwe-rescued boutons. Type Ib boutons (at rest: 4% Fwe, n = 23; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 15. Ten-minute 90 mM K+/2 mM Ca2+ stimulation: 4% Fwe, n = 20; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 23) derived from ≥3 larvae for each genotype were analyzed. (M) Data quantifications of the ratio of total synaptic vesicle (SV) area to bouton area. Type Ib boutons (4% Fwe, n = 11; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 11) derived from 3 larvae for each genotype were analyzed. (N–O) Confocal Z-projection images of NMJ boutons labeled with FM1-43 dye were obtained from 4% Fwe-rescued larvae (N) and 4% FweE79Q-rescued larvae (O). Larval fillets were stimulated with a chlorpromazine-containing solution as indicated in Fig 2K and 2L. Large membrane invaginations enriched with FM1-43 dye are marked by red arrows. (P) Data quantifications of the number of bulk membrane invaginations per bouton area. Chlorpromazine-induced bulk membrane invagination is impaired in 4% FweE79Q-rescued boutons when compared to 4% Fwe-rescued boutons. Type Ib boutons derived from A2/A3 muscles 4 or 6/7 were counted, and NMJs (4% Fwe, n = 17; and 4% FweE79Q, n = 26) derived from 5 larvae for each genotype were analyzed. A Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. p-Value: ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.001. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. Scale bar: 500 nm in A–J; 5 μm in N–O. The underlying data can be found in S1 Data.