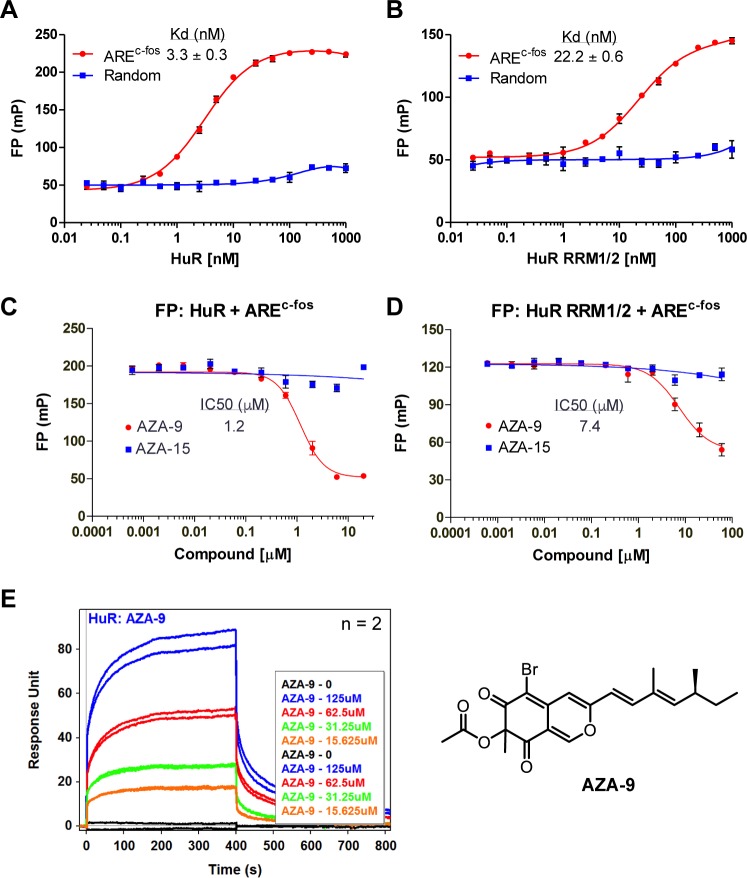
Fig 1. AZA-9 inhibits HuR-ARE RNA interaction and binds directly to HuR.
Titration of 2 nM AREc-fos and control RNA (a 16-nt fluorescein-labeled RNA oligo with random sequence) with (A) HuR and (B) HuR RRM1/2 (n = 3). (C) Dose-response curve of AZA-9 disrupting HuR-AREc-fos binding in FP assay using 10 nM HuR and 2 nM fluorescein-labeled AREc-fos (n = 3). (D) Dose-response curve of AZA-9 disrupting HuR RRM1/2-AREc-fos binding in FP assay using 50 nM HuR RRM1/2 and 2 nM fluorescein-labeled AREc-fos (n = 3). (E) SPR sensorgrams of AZA-9 injected at increasing concentrations of 0–125 μM into a flow cell containing immobilized HuR (n = 2). Structure of AZA-9 is shown on the right. The following were the negative controls used–random RNA in (A) and (B); and AZA-15 in (C) and (D).