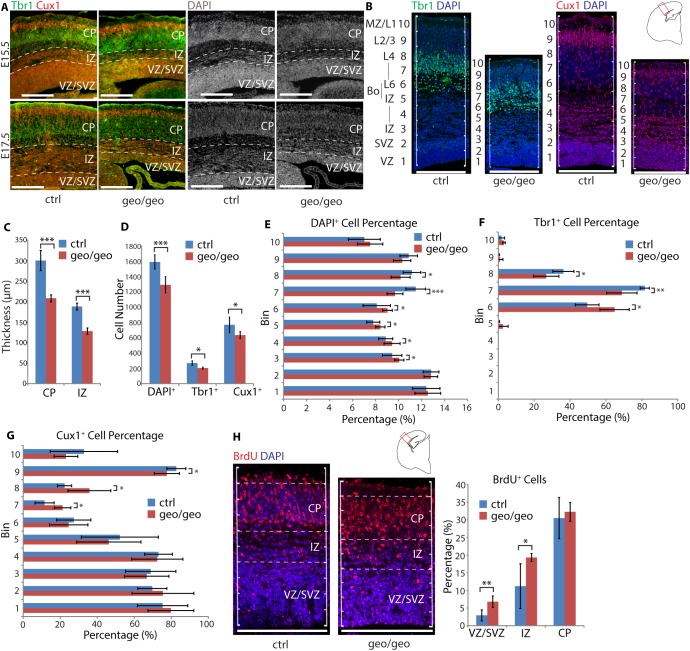
Fig 5. Loss of BIG1 causes accumulation of excitatory neurons before destination layers.
(A) The layering order of UL neurons (Cux1+) and DL neurons (Tbr1+) was maintained in Arfgef1geo/geo but the IZ thickness reduced at E17.5. Scale bars, 200 μm. n = 3 per group. (B) At E17.5, the numbers of Tbr1+, Cux1+ and DAPI+ cells within a 200 μm cortical width starting from the edge of the lateral ventricle were counted. Scale bars, 200 μm. n = 4 per group. (C) The thickness of the CP (***p = 0.0003) and IZ (***p = 1.25E-06) in Arfgef1geo/geo brains were significantly reduced. n = 5 per group. (D) In Arfgef1geo/geo neocortex, the total Tbr1+ (*p = 0.02), Cux1+ (*p = 0.04) and DAPI+ (***p = 0.0007) cells per 200 μm cortical width significantly reduced compared to controls. Tbr1+, n = 4 per group; Cux1+, n = 4 per group; DAPI+, n = 8 per group. (E) In Arfgef1geo/geo neocortex, DAPI+ cells accumulated in Bin 3 (*p = 0.02), Bin 4 (*p = 0.04), Bin 5 (*p = 0.03), Bin 6 (*p = 0.03) at the expense of DAPI+ cells in Bin 7 (***p<0.0001), and Bin 8 (*p = 0.01). n = 8 per group. (F) In the Arfgef1geo/geo neocortex, Tbr1+ cells accumulated in Bin 6 (*p = 0.01) and at the expense of Tbr1+ cells in Bin 7 (**p = 0.004) and Bin 8 (*p = 0.03). n = 4 per group. (G) The Cux1+ cells accumulated in Bin 7 (*p = 0.01) and Bin 8 (*p = 0.03) at the expense of Cux1+ cells in Bin 9 (*p = 0.02). n = 4 per group. (H) Pregnant dams at E12.5 were injected with BrdU and the migration of cells in neocortex was quantified at E15.5. The percentage of BrdU+ cells in the VZ/SVZ (**p = 0.007) and IZ (*p = 0.04) significantly increased in Arfgef1geo/geo compared to control brains. However, the percentage of BrdU+ cells in CP (p = 0.31) did not decrease. Arfgef1geo/geo, n = 2; controls, n = 4. For all bar graphs, Student’s T-test was used for comparisons between groups. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. Bo, IZ-CP boundary; CP, cortical plate; IZ, intermediate zone; L1-L6, layers 1–6, MZ, marginal zone; VZ/SVZ, ventricular zone and subventricular zone.