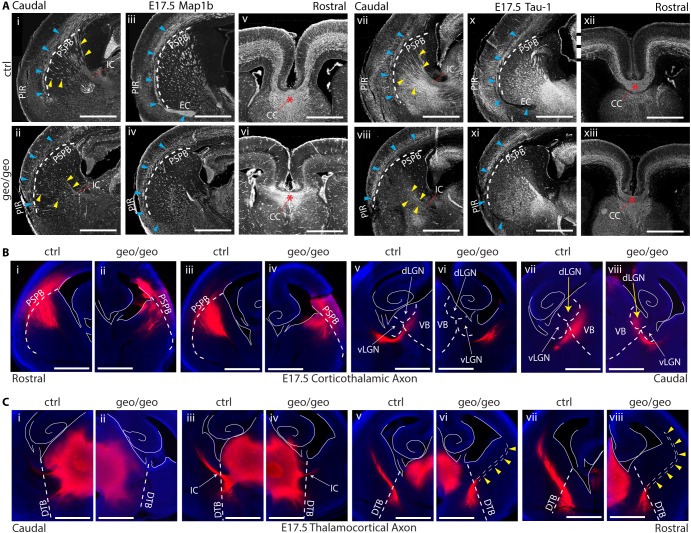
Fig 6. Loss of BIG1 causes defects in axonal projection, axonal pathfinding and axonal extension.
(A) At E17.5, there are differences in the projecting direction of cortical axons (blue arrowheads) and in the numbers of axon fascicles passing the PSPB (yellow arrowheads) in Arfgef1geo/geo brains compared to controls. The CC (red asterisks) in Arfgef1geo/geo forebrain has no difference compared to the control. Scale bars, 500 μm. n = 3 per group. (B) DiI tracing of shows a pathfinding defect of corticothalamic axons in Arfgef1geo/geo brains. Scale bars, 500 μm. n = 3 per group. (C) DiI tracing of thalamocortical axons shows an axonal extension defect in Arfgef1geo/geo thalamic neurons. Scale bars, 500 μm. n = 3 per group. PSPB, pallial-subpallial boundary; CC, corpus callosum; DTB, diencephalon-telencephalon boundary; IC, internal capsule; vLGN, ventral lateral geniculate nucleus; VB, ventrobasal complex; dLGN, dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus.