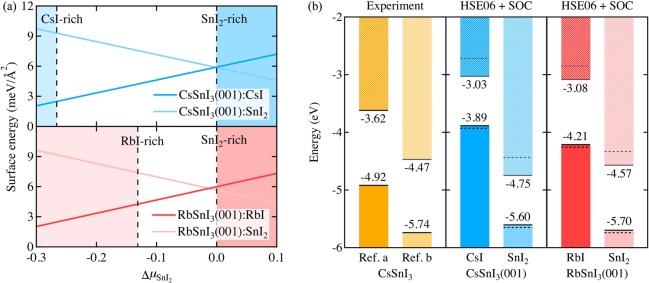
Figure 5.
(a) Calculated surface energy as a function of the change in the SnI2 chemical potential (ΔμSnI2) for all surface terminations of CsSnI3(001) and RbSnI3(001). ΔμSnI2 for CsI-, RbI-, and SnI2-rich conditions are determined as −0.27, −0.13, and 0 eV, respectively. (b) Band energy level alignment diagrams: EVBM and ECBM levels from experiments (for CsSnI3)21,22 and HSE06+SOC calculated values for CsSnI3(001) and RbSnI3(001). All energy levels are aligned with respect to the absolute vacuum level (set to 0 eV). The energy levels in horizontal solid and dashed lines refer to the HSE06-calculated EVBM and ECBM levels with and without consideration of the SOC effect, respectively.