Figure 6. siRNA-mediated knockdown of FUS and YB-1 expression inhibits endogenous COXIV mRNA trafficking and translation in rat sympathetic axons.
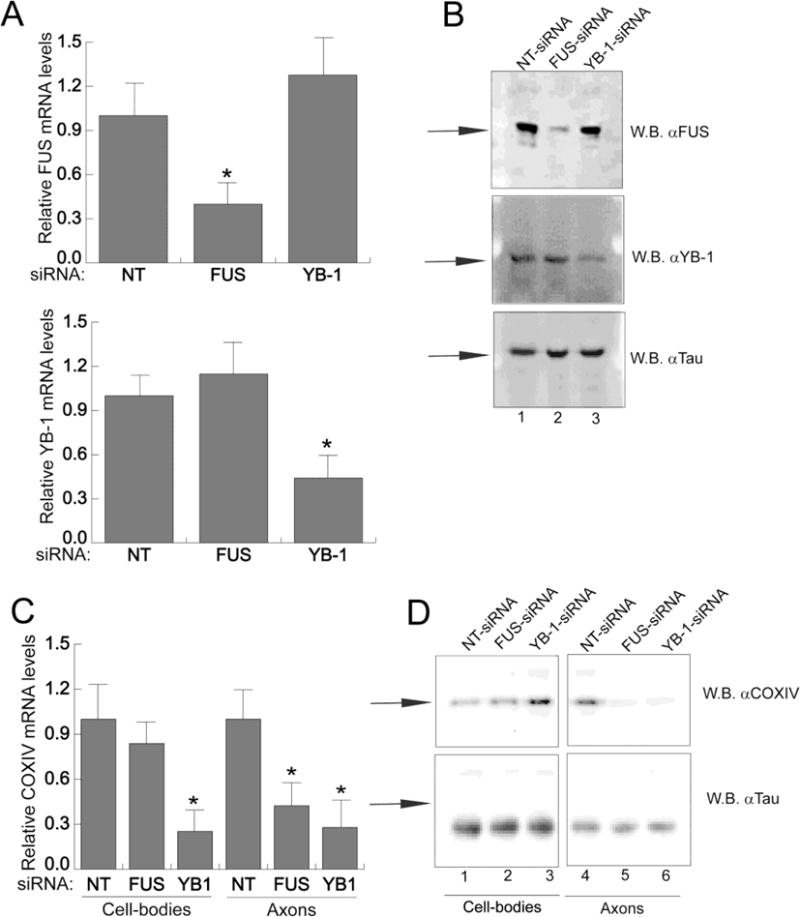
siRNA oligonucleotides (100pmoles) targeted against either FUS or YB-1 or nontargeting NT-siRNA were transfected into the cell-body compartments of 1-week-old SCG neurons. After transfection (36h), cell-bodies and axonal compartments were lysed and RNA and protein levels were assessed by qRT-PCR and western blot analyses, respectively (A and B). The FUS and YB-1 mRNA levels from cell bodies were measured by qRT-PCR (A) and cell-body protein levels visualized by Western analyses (B). The mRNA levels are expressed relative to RPS18 mRNA, and Tau protein levels served as a loading control for the western analyses. Arrows indicate specific western bands. Values represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA and post-hoc test). Each experiment was repeated three times with similar results
