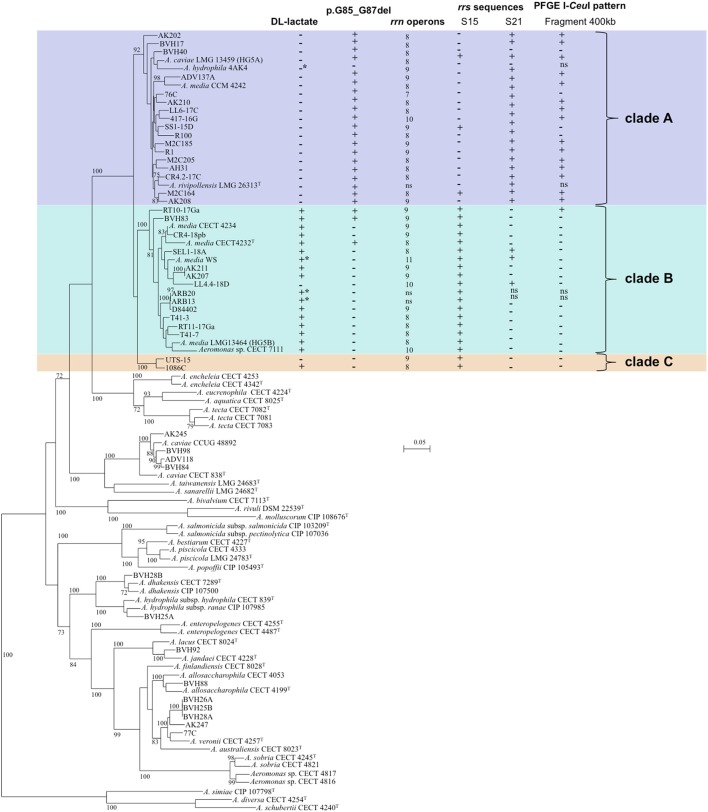
Figure 1.
Unrooted Maximum-Likelihood tree based on concatenated sequences of 16 housekeeping gene fragments (9,427 nt.) from 3 MLST schemes. The tree shows the phylogenetic structure of the studied Media species complex population and the relative placement of strains to other recognized species in the genus. The horizontal lines represent genetic distance, with the scale bar indicating the number of substitutions per nucleotide position. The numbers at the nodes are support values estimated with 100 bootstrap replicates. Only bootstrap values ≥70 are indicated. The following characteristics are indicated for strains affiliated to A. media from left to right: (i) DL-lactate utilization, (ii) presence/absence of a 3 amino acid deletion (p.G85_G87del†), corresponding to a deletion of 9 nucleotides (c.3357226_3357234del††), (iii) number of rrn operons, (iv) presence/absence of 16S rRNA gene sequences S15 and/or S21 (corresponding to PCR-TTGE bands No. 15 and/or No. 21) revealed either by analysis of WGS or PCR-TTGE pattern, (v) presence/absence of DNA fragment of about 400 kb in PFGE I-CeuI pattern. The type strain of Aeromonas fluvialis was not included in the phylogenetic tree either because we failed to amplify the locus ppsA. This species did not group with Media complex in a 7 gene (atpD, dnaJ, dnaX, gyrA, gyrB, recA, rpoD)-based tree. *DL-lactate utilization or absence inferred from genomic analysis; +, positive; −, negative; ns, not studied. †position on the chaperone protein DnaJ sequence of A. hydrophila subsp. hydrophila ATCC 7966T (GenBank ABK39448.1). ††position on the circular chromosome sequence of A. hydrophila subsp. hydrophila ATCC 7966T (NCBI Reference Sequence NC_008570.1).