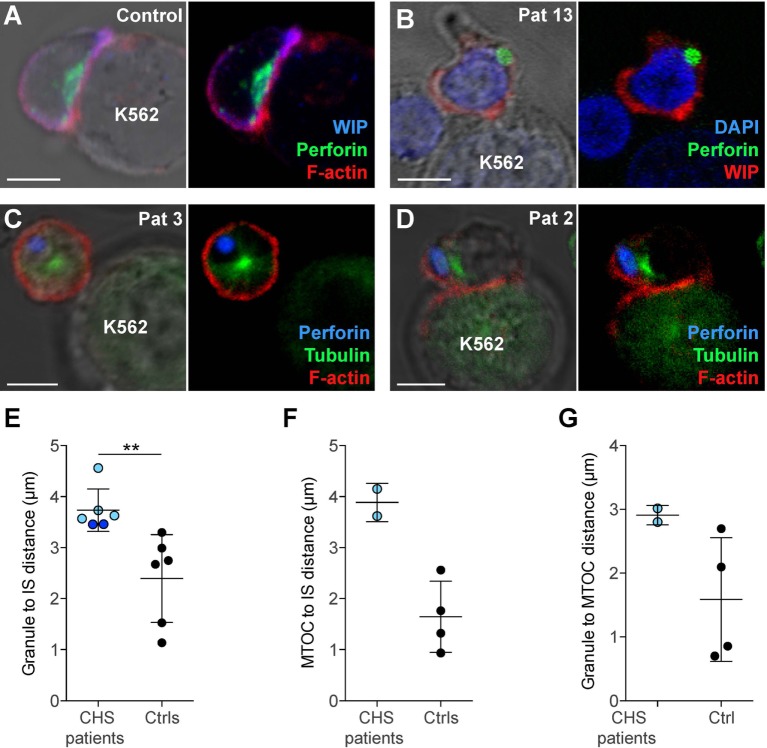
Figure 5.
Chediak–Higashi syndrome (CHS) patient NK cells form conjugates with target cells, but granules and microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) do not efficiently polarize to the immune synapse (IS). (A) A representative NK cell from a healthy donor conjugated to a K562 target cell, labeled with antibodies to WASP-interacting protein (WIP) and perforin as well as phalloidin to detect F-actin, as indicated. (B) A representative NK cell from a CHS patient conjugated to a K562 cell, labeled with antibodies to WIP and perforin, in addition to DAPI to discern the nucleus, as indicated. (C–D) NK cells from CHS patients conjugated to K562 cells, labeled with antibodies to perforin and tubulin as well as phalloidin to detect F-actin, as indicated. (A–D) Scale bars indicate 5 μm. Distances were measured between (E) MTOC and IS, (F) granules and IS (center of the contact between NK cell and target cell), or (G) granule and MTOC. (E–G) Each symbol represents average values from multiple cells from individual patients and controls, with overall mean and SD indicated. (E) 45 (range 9–150) CHS patient and 266 (range 54–488) control NK cells and (F,G) 17 (range 16–18) CHS patient and 269 (range 201–325) control NK cells were quantified.