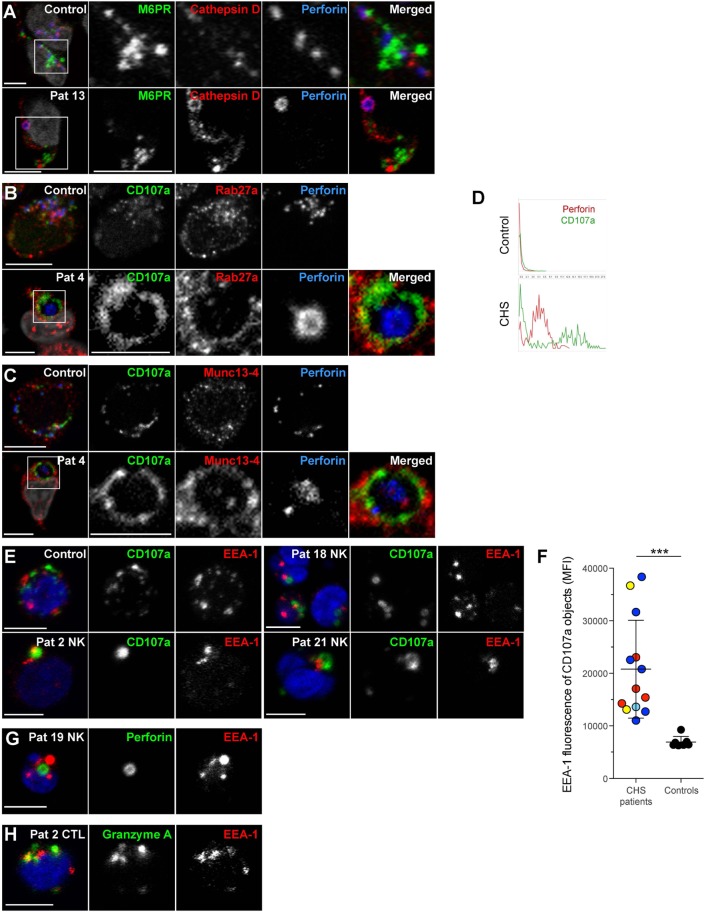
Figure 6.
Chediak–Higashi syndrome (CHS) NK cell granules are positive for Munc13-4, Rab27a, CD107a, cathepsin D, and EEA1, but not mannose-6-phosphate receptor. Freshly isolated NK cells were labeled for perforin, DAPI and (A) M6PR and cathepsin D, (B) CD107a and Rab27a, or (C) CD107a and Munc13-4. (D) Traces show perforin and CD107a staining along a transect of a representative cytotoxic granule in a NK cell from (top panel) healthy control individual as well as (bottom panel) CHS patient, respectively. (E) Freshly isolated NK cells from a healthy control and three CHS patients with various LYST mutation positions were labeled for CD107a, EEA1, and DAPI, as indicated. (F) EEA1 median fluorescence intensity (MFI) within CD107a-positive objects was quantified in healthy control and CHS patient NK cells. On average 90 (range 8–187) CHS patient and 85 (range 42–135) control NK cells were quantified. (G) Freshly isolated NK cells from a CHS patient labeled for perforin, EEA1, and DAPI, as indicated. (H) Freshly isolated T cells from a CHS patient labeled for granzyme A, EEA1, and DAPI, as indicated. In micrographs, scale bars indicate 5 μm.