Figure 2. CK2 phosphorylates Olig2 at S13.
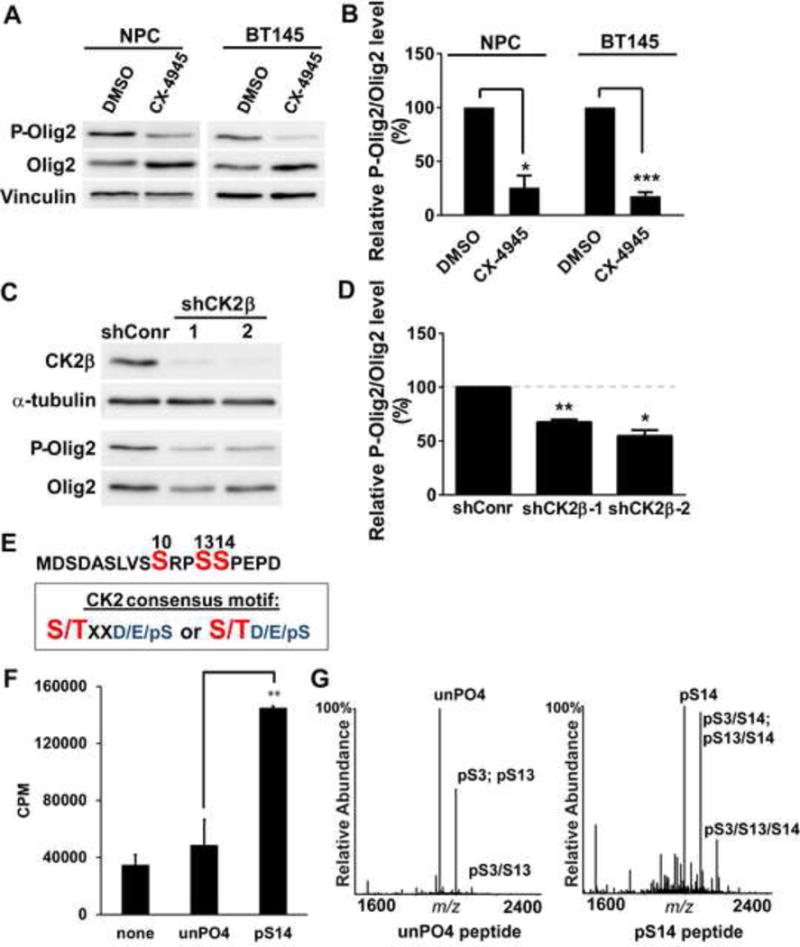
(A) Immunoblot assay. Mouse NPCs and BT145 human glioma cells were treated with the CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 (20 μM) for 4 hours. Cell lysates were size fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotted with P-Olig2 and Olig2 antibodies. (B) Quantification of immunoblot assays. Relative P-Olig2/Olig2 levels were quantified and compared between control and inhibitor-treated group. Data were analyzed by t-test and are represented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 and ***p<0.001, n=3. (C) Genetic validation of inhibitor data. CK2β was knocked down in wild-type mouse NPCs by lentiviral vectors that express shRNAs targeting mCK2β. Cells that were stably transduced with lentivirus that encode non-target shRNA served as a control (shConr). (D) Quantification of knock-down data. Relative P-Olig2/Olig2 levels were quantified and compared between the knockdown group and control group. Data were analyzed by t-test and are represented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01, n=3. (E) CK2 consensus motif fits S13 site. S/T (highlighted with red), the kinase’s target Serine/Threonine residue; X, could be any amino acid; pS, phosphorylated serine; D, aspartic acid; E, glutamic acid. (F) in vitro kinase assay demonstrates that CK2 phosphorylates the Olig2 N-terminal peptide, and this phosphorylation is facilitated by the phosphorylation of S14. Synthetic Olig2 N-terminal peptides (a.a.1–18) were generated without phosphorylation (unPO4) and with pre-phosphorylation at S14 (pS14). Reactions without peptides (none) served as negative control. Data were analyzed by t-test and are represented as mean ± SEM. n=3; **p<0.01. (G) Mapping CK2 phosphorylation sites by mass spectrometry analysis. in vitro kinase reactions were analyzed by MALDI-MS and −MS/MS. Peaks shown are pS3 (singly phosphorylated peptide at S3); pS13 (singly phosphorylated peptide at S13); pS3/S13 (doubly phosphorylated peptide at S3 and S13); pS3/S14 (doubly phosphorylated peptide at S3 and S14); pS13/S14 (doubly phosphorylated peptide at S13 and S14); pS3/S13/S14 (triply phosphorylated peptide at S3, S13 and S14).
