Figure 7. Therapeutic potential of an Olig2 kinase antagonist in a murine model of pediatric low-grade astrocytoma.
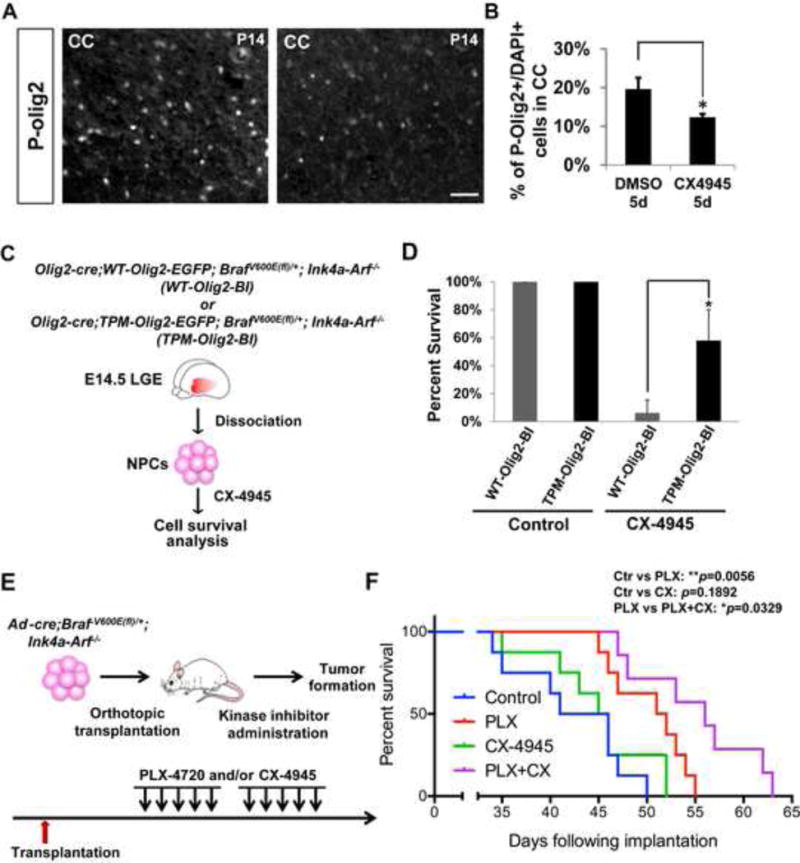
(A and B) CK2 inhibition decreases P-Olig2 level in vivo. Developing hGFAP-cre; BrafV600E(fl)/+; Ink4a-Arf−/− pups were treated with CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 25 mg/kg intraperitoneally for 5 days and were analyzed at P14. CC, Corpus Callosum. Scale bar, 50μm. Data are represented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, n=3. (C) Schematic diagram shows generation of two BRAFV600E-transformed NPC lines in an Ink4a-Arf−/− background. The two lines express knock-in, epitope-tagged Olig2 wherein the triple serine motif is either wild type (WT-Olig2-BI) or triple phosphomimetic with the S10D/S13E/S14D substitutions (TPM-Olig2-BI). Of note, the Olig2-cre driver is used to activate expression of the BRAFV600E oncogene, while simultaneously disrupting another endogenous Olig2 allele (Schuller et al., 2008). The resulting mice exhibit early prenatal lethality, which precludes further study in postnatal pups. (D) Proliferation of the TPM-Olig2-BI line is partially resistant to the CK2 antagonist CX-4945. For proliferation assays, 5×104 cells were seeded at Day 0 and 1μM of CX-4945 was added at Day 1. The cell number was assessed at Day 4. Data were analyzed by t-test and represented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, n=3. (E) Schematic diagram demonstrates orthotopic transplantation and the treatment regimen (see Experimental Procedures). (F) Combination of BRAF and CK2 inhibitors significantly improves survival in an orthotopic model of pediatric glioma. Kaplan-Meier graph is illustrated and Log-rank test was used to determine the survival differences between different treatment groups. *p<0.05, and **p<0.01; n=8.
