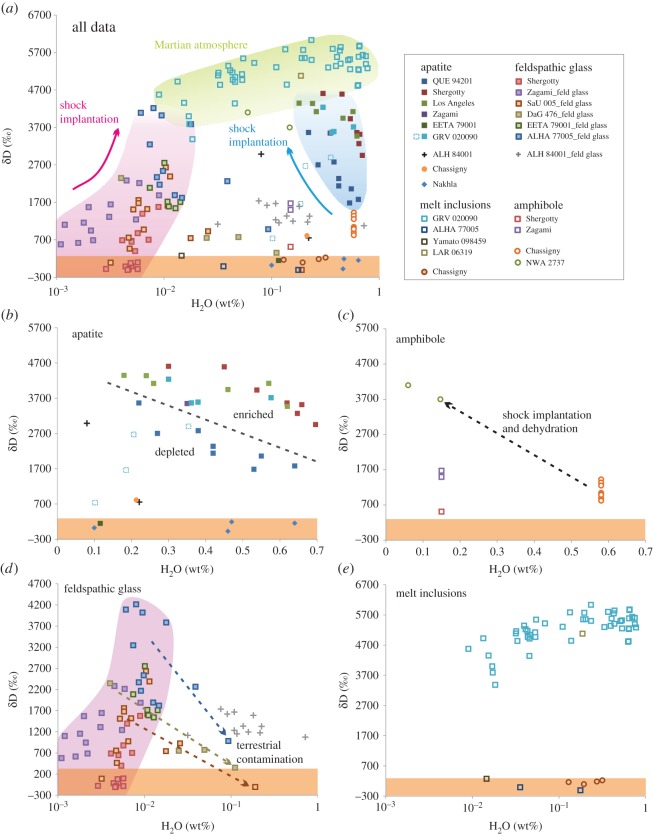
Figure 3.
(a–e) D/H ratio (δD) versus water content in Martian igneous minerals. High-impact shock pressures, mantle source enrichment and crustal assimilation can add D-rich atmospheric hydrogen to igneous minerals, meaning the majority do not have D/H ratios representative of the Martian mantle (δD < 275‰, orange envelope). See the electronic supplementary material for data and references.