FIG 10.
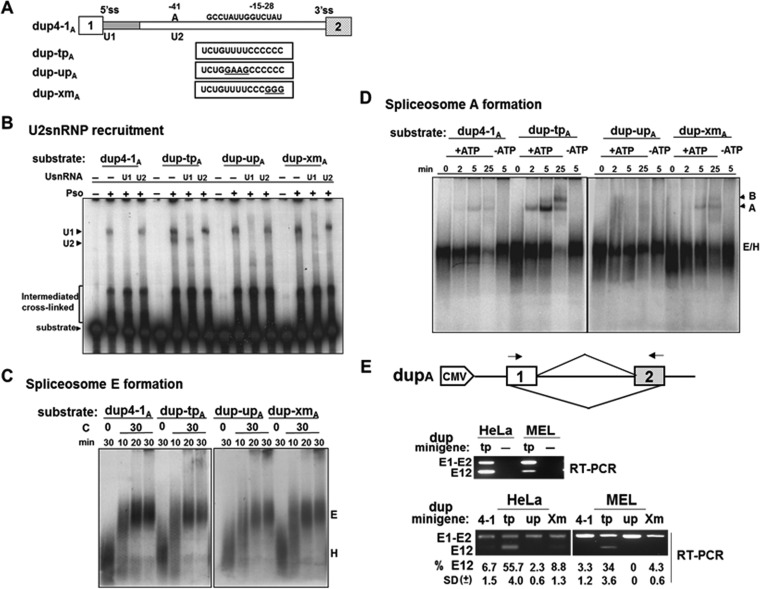
TIA1 and Pcbp1 binding sequences are required for U2 snRNP recruitment and spliceosome A complex formation. (A) Schematic representation of a single intron template containing exon 1 through exon 2 of DUP4-1 and its mutant derivatives. RNA substrates containing the wild type (dup4-1A), both TIA1 and Pcbp1 binding sequences (dup-tpA), a mutated TIA1 site (dup-upA), and a mutated Pcbp1 site (dup-xmA) are represented. (B) Psoralen-dependent cross-linked species detected after incubation of 32P-labeled RNA substrates in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. The identity of the cross-linked species was determined by hybridizing nuclear extracts to DNA complementary to positions 1 to 15 of U1 snRNA or 28 to 42 of U2 snRNA, followed by RNase H digestion before cross-linking. The positions of free substrates, U1 snRNA, and U2 snRNA cross-linked complexes are indicated. (C) Neither TIA1 nor Pcbp1 binding sequence affects E complex formation. RNA transcripts were incubated in ATP-depleted HeLa cell nuclear extracts and incubated at 0°C or 30°C for the indicated times, fractionated on 1.5% low-melting-point agarose gels, fixed, dried, and exposed to X-ray film. Prespliceosomal H and E complexes are indicated. (D) TIA1 and Pcbp1 binding sequences activate spliceosomal A complex formation. Transcripts were incubated in ATP-depleted (−ATP) or nondepleted (+ATP) HeLa cell nuclear extracts at 30°C for the indicated times and processed as described for panel C. Prespliceosomal H and E (H/E) complexes as well as A and B complexes are indicated. (E) Correlation between U2 snRNP recruitment/spliceosomal A complex formation and splicing efficiency. The top panel shows a schematic representation of the dup minigene construct. Primers used in RT-PCR are indicated by arrows. RT-PCR primers are minigene specific (middle panel). RNA was isolated from dup-tpA transfected (tp) and untransfected (−) cells after 40 h and analyzed by RT-PCR. dup4-1A and its mutant constructs were transfected into HeLa or MEL cells and analyzed for unspliced (E1-E2) and spliced (E12) products (bottom panel). Splicing efficiency was calculated as the percentage of total RNA products containing spliced E12. Averages and SDs were obtained for three independent experiments (n = 6), and results are presented at the bottom of each lane. CMV, cytomegalovirus.