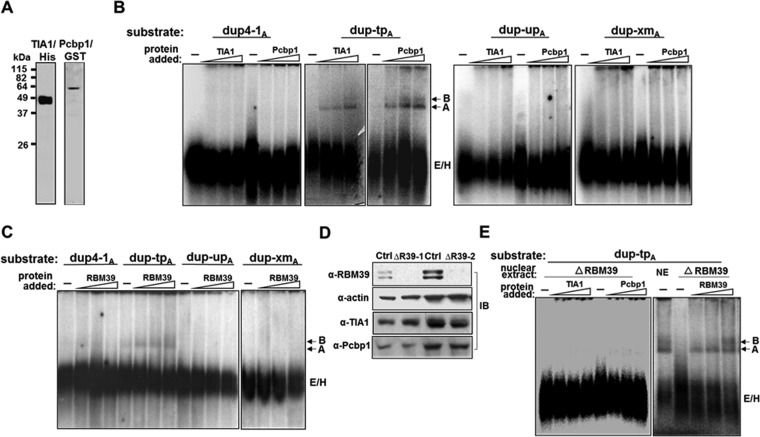
FIG 11.
TIA1 and Pcbp1 activation of spliceosomal A complex formation is RBM39 dependent. (A) Purified TIA1/His and Pcbp1/GST proteins. (B and C) TIA1, Pcbp1, and RBM39 enhance spliceosome A complex formation on a dup-tpA substrate containing TIA1 and Pcbp1 binding sequences. TIA1 or Pcbp1 (B) or RBM39 (C) was added at increasing concentrations into each substrate, and complex formation was analyzed. Prespliceosomal E/H complexes as well as A and B complexes are indicated. −, probe alone. (D) Validation of RBM39 silencing. Lysates from HeLa cells treated with a control (Ctrl) or RBM39 siRNA (siRBM39-1 and siRBM39-2) were analyzed for RBM39 knockdown with an anti-RBM39 antibody. Anti-TIA1 and anti-Pcbp1 antibodies detected their respective proteins. β-Actin served as a loading control. (E) RBM39-dependent A complex formation. RBM39 silencing reduces the effect of TIA1 and Pcbp1 on A complex formation (left panel). TIA1 or Pcbp1 was added at increasing concentrations into RBM39-depleted HeLa cell nuclear extracts (ΔRBM39) with dup-tpA substrate and analyzed for complex formation. RBM39 reconstituted complex A formation when added back to depleted nuclear extracts (right panel). −, probe alone.