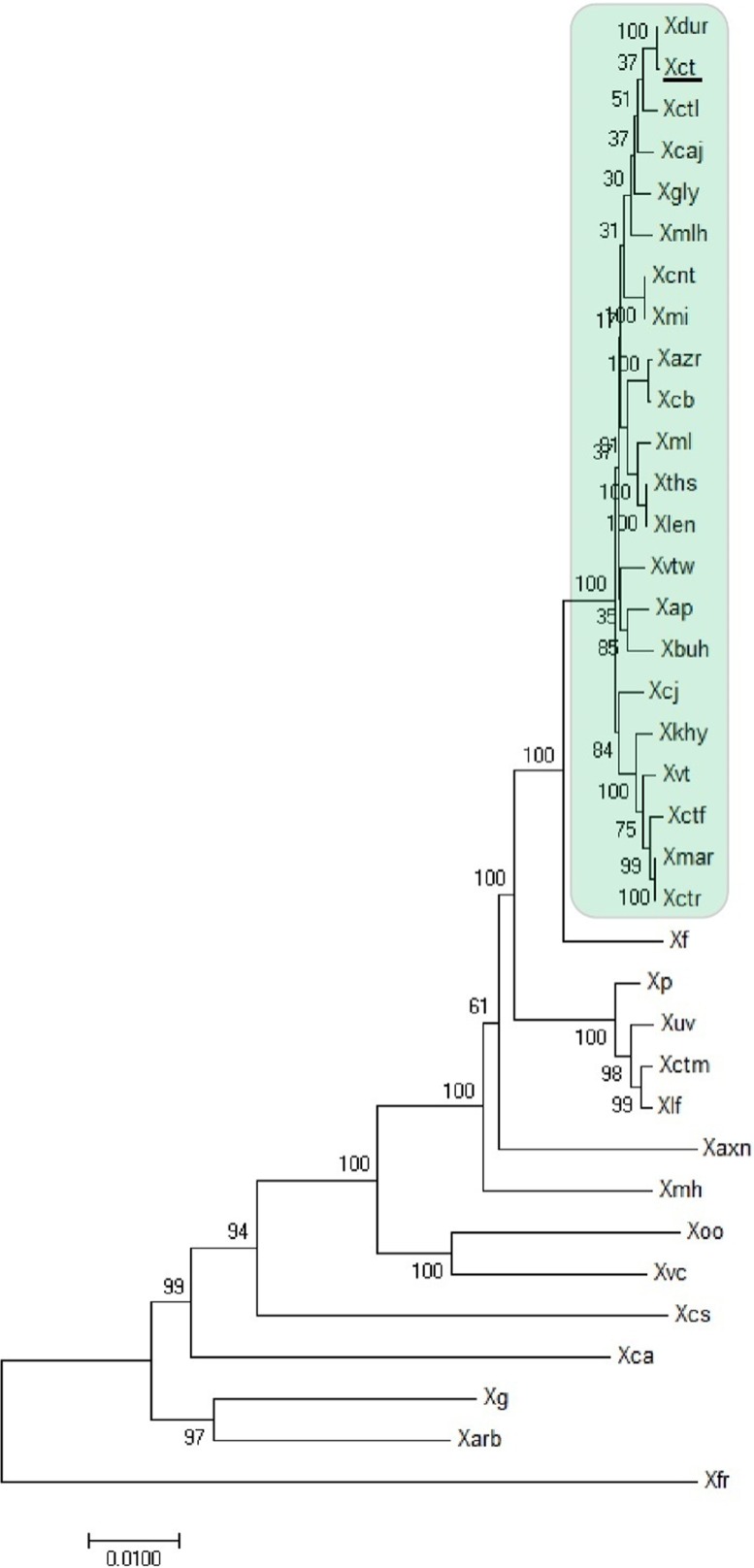
FIG 1.
Maximum likelihood tree of different Xanthomonas species and pathovars infecting diverse hosts constructed using 28 reference genes with 500 bootstrap replications. The scale bar shows the number of nucleotide substitution per site. The “type strain,” X. citri pv. citri LMG 9322T (Xct), is underlined. The strains in the green box consist of Xanthomonas pv. strains forming a clade with X. citri pv. citri LMG 9322 (denoted as XCPs). Abbreviations: Xvtw, X. campestris pv. vitiswoodrowii LMG 954; Xbuh, X. axonopodis pv. bauhiniae LMG 548; Xmar, X. axonopodis pv. martyniicola LMG 9049; Xctr, X. campestris pv. vitiscarnosae LMG 939; Xvt, X. campestris pv. viticola LMG 965; Xctf, X. campestris pv. vitistrifoliae LMG 940; Xkhy, X. axonopodis pv. khayae LMG 753; Xcj, P. cissicola LMG 21719; Xmlh, X. axonopodis pv. melhusii LMG 9050; Xcb, X. campestris pv. bilvae NCPPB 3213; Xazr, X. campestris pv. azadirachtae LMG 543; Xap, X. axonopodis pv. punicae LMG 859; Xdur, X. campestris pv. durantae LMG 696; Xct, X. citri pv. citri LMG 9322; Xcaj, X. axonopodis pv. cajani LMG 558; Xctl, X. axonopodis pv. clitoriae LMG 9045; Xmi, X. campestris pv. mangiferaeindicae LMG 941; Xcnt, X. campestris pv. centellae LMG 9044; Xgly, X. citri pv. glycines LMG 712; Xml, X. citri pv. malvacearum LMG 761; Xths, X. campestris pv. thespesiae LMG 9057; Xlen, X. campestris pv. leeana LMG 9048; Xf, X. fuscans pv. fuscans NCPPB 381; Xp, X. perforans 91-118; Xuv, X. euvesicatoria LMG27970; Xctm, X. axonopodis pv. citrumelo F1; Xlf, X. alfalfae subsp. alfalfae LMG 495; Xaxn, X. axonopodis DSM 3585; Xmh, X. axonopodis pv. manihotis LMG 784; Xoo, X. oryzae ATCC 35933; Xvc, X. vasicola NCPPB 2417; Xcs, X. cassavae CF BP 4642; Xca, X. campestris pv. campestris ATCC 33913; Xg, X. gardneri ATCC 19865; Xarb, X. arboricola pv. juglandis strain CF BP 2528; Xfr, X. fragariae LMG 25863. Except for the 18 genomes sequenced in-house (Table 2), all of the genomes were from databases.