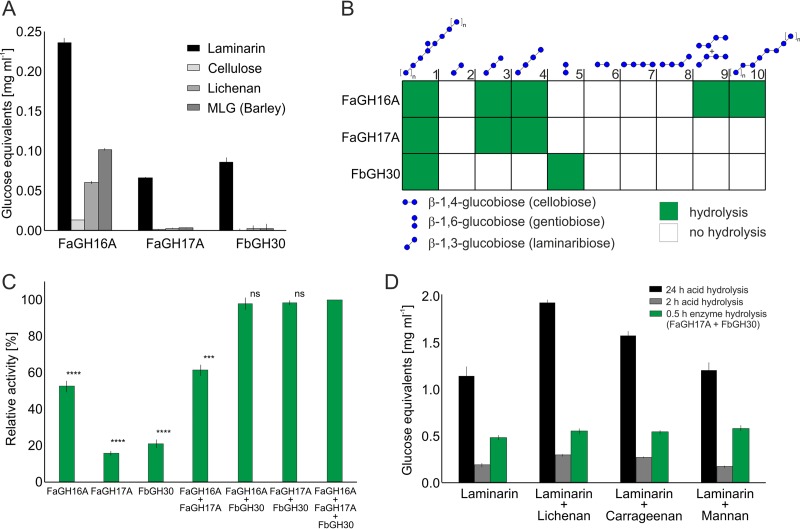
FIG 3.
Glycoside hydrolases showing different levels of specificity for laminarin and related glucans. (A) Activity tests with glucan polysaccharides and oligosaccharides containing β-1,3, β-1,4, and β-1,6 linkages, based on the PAHBAH reducing sugar assay. Shown are mean and standard deviation (SD) values from three technical replicates. (B) Enzyme specificity tested with defined oligosaccharide substrates, using thin-layer chromatography. The results are presented as a heatmap (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). The substrates at 0.1% (wt/vol) were hydrolyzed for 30 min at 37°C by 100 nM (∼5 μg ml−1) purified enzyme in PBS buffer at pH 7.5. (C) Mixtures of FbGH30 and FaGH17A or FbGH30 and FaGH16A, showing greater activity than the individual enzymes. The highest activity level with all three enzymes was set to 100%, and all other samples were compared to that value. Laminarin at 0.1% (wt/vol) was hydrolyzed for 30 min at 37°C by 100 nM (∼5.0 μg ml−1) of each purified enzyme in PBS buffer at pH 7.5, and hydrolysis was measured with the PAHBAH assay. Shown are mean and SD values from three technical replicates. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001, independent two-sample Student's t test. ns, not significant. (D) Comparison of hydrolysis yields of enzymatic, partial acid, and total acid hydrolysis of different polysaccharides. Lichenan, carrageenan, and mannan at 0.1% (wt/vol) were added to 0.1% (wt/vol) laminarin and were hydrolyzed for 30 min at 37°C with 100 nM purified enzyme (∼5 μg ml−1 of FaGH16A, FaGH17A, or FbGH30) in 50 mM MOPS buffer. Boiling for 5 min at 100°C stopped the reaction. Partial acid hydrolysis was conducted for 2 h at 20°C with 50 mM H2SO4. Total acid hydrolysis was carried out for 24 h at 100°C with 1 M HCl. The reaction mixtures were analyzed with the PAHBAH assay. All experiments were carried out in triplicate. Shown are mean and SD values from three technical replicates.