Figure 8. Development, immunogenicity and efficacy of the Rv21 virus-like particle (VLP) presenting the PvCSPVK210/247 antigen fused to the Hepatitis B Surface antigen.
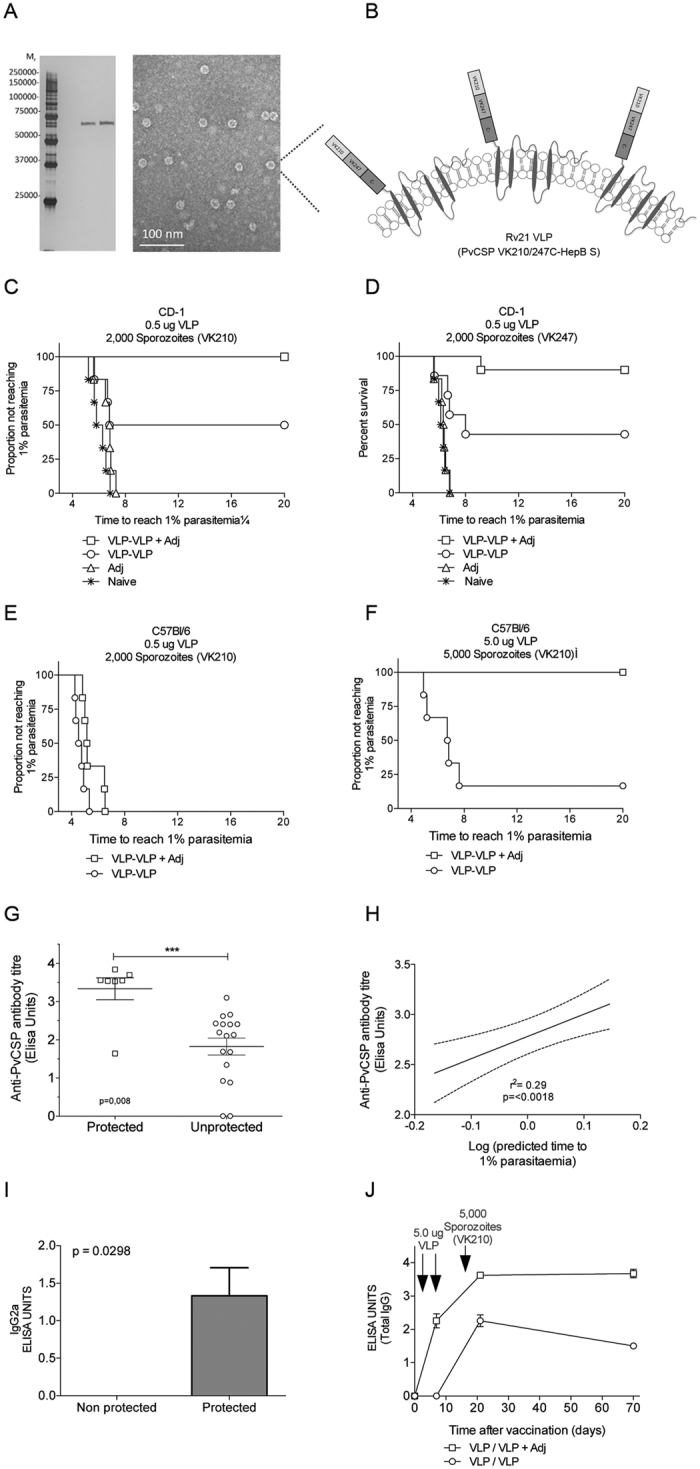
The chimeric construct was expressed as a VLP in P. pastoris. (A) Analysis of protein purity using silver staining after two purification rounds, using size exclusion chromatography of 10 ng of elution sample (A and B), and visualization of VLPs, by TEM (right panel). (B) Diagram showing the proposed structure of Rv21. (C) Protective efficacy of Rv21 in CD-1 mice (n = 6) immunized using prime-boost at low doses of 0.5 ug of VLP alone or mixed with Matrix M adjuvant and challenged with transgenic sporozoites expressing P. vivax CSP VK210 or (D) VK247. Kaplan-Meier curves indicate the time to reach 1% parasitaemia. (E) Protective efficacy in C57Bl/6 mice (n = 6) immunized using prime-boost, either a low dose of 0.5 ug or a (F) high dose of 5 ug (right) of Rv21 in presence or absence of Matrix M adjuvant (Adj). Challenge of mice vaccinated with 5 ug was increased to 5,000 spz/mouse to increase stringency. Mice were challenged with transgenic sporozoites expressing P. vivax CSP VK210 or VK247. The Kaplan-Meier curves illustrate the time to 1% parasitaemia. (G) Association and (H) correlation of total IgG antibody titers with protective efficacy using data of sera from VK210-challenged C57Bl/6 mice. (I) Association of titers of IgG2a with efficacy against pre-erythrocytic malaria. (J,G) Kinetic of the antibody responses in presence or absence of the Matrix M adjuvant.
