Fig. 7.
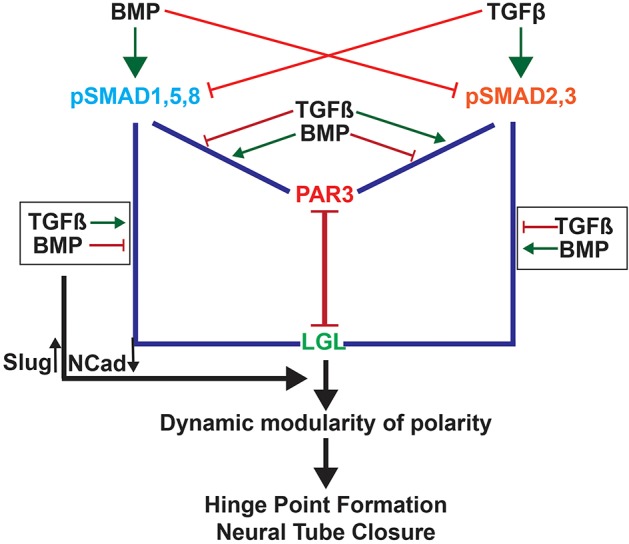
Cartoon summarizing cell-cycle-dependent TGF–BMP polarity interactions in regulating MHP formation. BMP signaling induces SMAD1,5,8 phosphorylation and reduces SMAD2,3 phosphorylation. This increases pSMAD1,5,8–PAR-complex interactions and reduces pSMAD2,3–PAR-complex interactions at apical junctions. BMPs also increase pSMAD2,3–LGL interactions and reduce pSMAD1,5,8–LGL interactions. Together these interactions create a stable epithelium. TGFβ signaling has the opposite effect and can disrupt epithelial organization and tight junction integrity either by increasing pSMAD2,3–PAR-complex interactions or decreasing pSMAD2,3–LGL interactions. Each cell cycles between the two states in a cell-cycle-dependent manner, giving rise to a dynamic epithelium capable of cell-shape changes, while retaining overall epithelial integrity. In addition, BMP and TGFβ signaling can modulate SLUG and NCAD expression in opposite directions, potentially through canonical mechanisms.
