Figure 5.
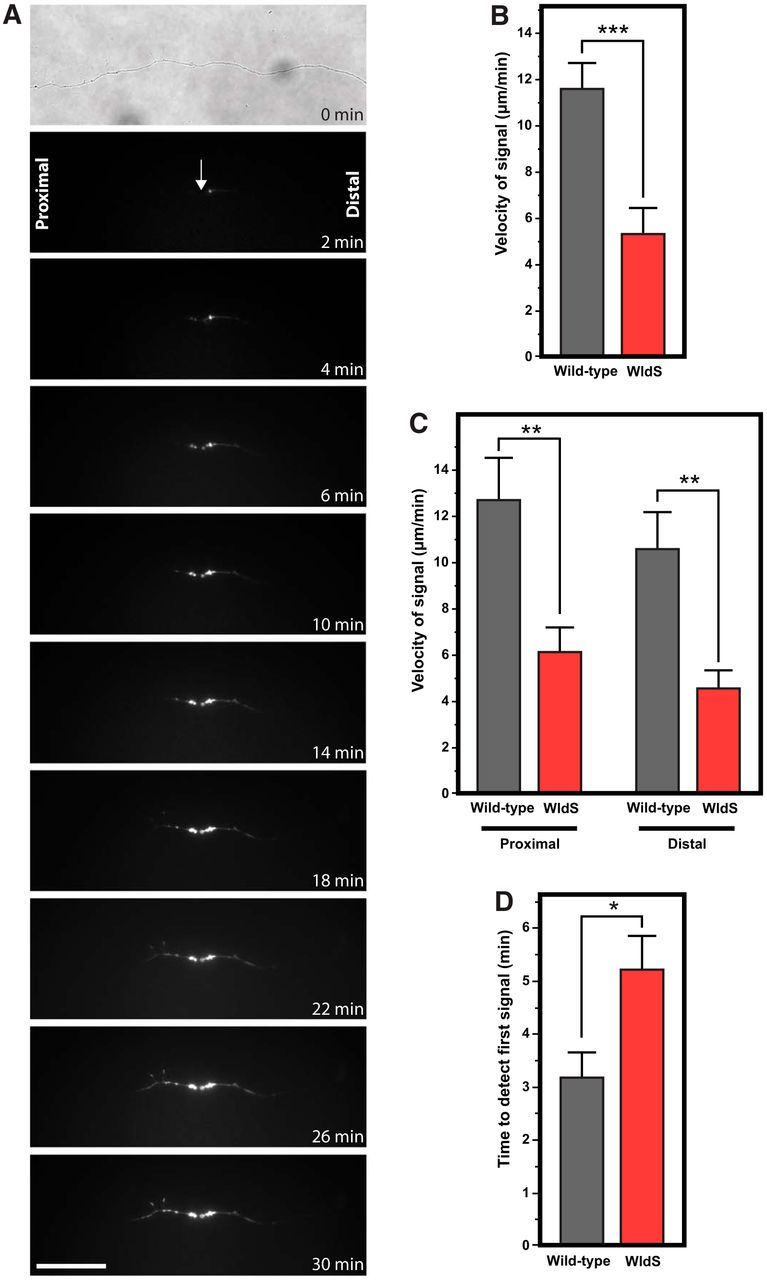
Phosphatidylserine externalization propagates more slowly along transected WldS axons compared with wild-type axons. A, Time-lapse series of images from a transected WldS axon show significantly slower propagation of phosphatidylserine externalization. B, WldS-transected axons had significantly slower phosphatidylserine externalization compared with wild-type axons. C, Slowed velocity of phosphatidylserine externalization was seen in both the proximal and distal axon segments. D, Compared with wild-type axons, there was a significantly longer delay before the onset of phosphatidylserine externalization signal in WldS axons. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Scale bar, 40 μm.
