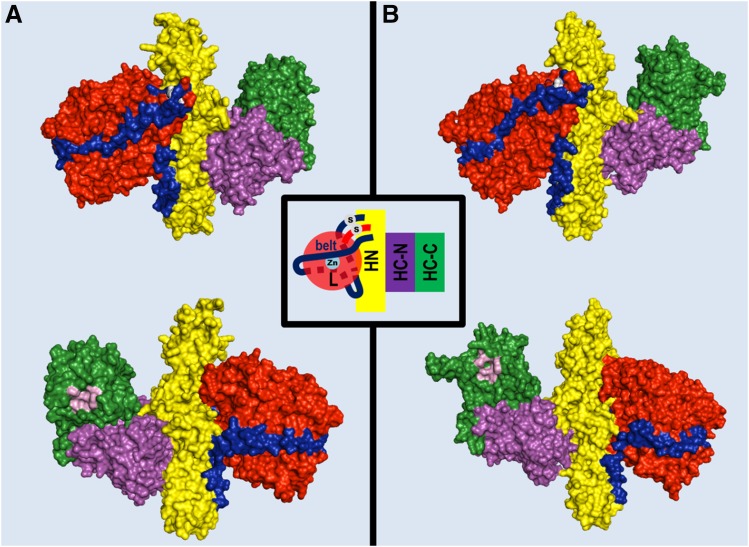
Fig. 1.
Structure of BoNT/A1 and BoNT/B1 molecules. Crystal structures of BoNT/A1 (PDB ID: 3BTA) (Lacy et al., 1998) (A) and BoNT/B1 (PDB ID: 1EPW) (Swaminathan and Eswaramoorthy, 2000) (B) represented as space-filling models of the two opposite surfaces of each toxin molecule showing the organization of the three toxin domains: the neurospecific binding HC-C subdomain (green), the lectin-like HC-N subdomain (purple), the translocation HN domain (yellow), and the metalloprotease L domain (red). The pink cavity in the HC-C subdomains shown in the lower panels is the polysialoganglioside binding site. A peptide belt (shown in blue) surrounding the L domain and the interchain disulfide bond (white in the upper panels) linking the L and HN domain, which stabilize the structure, is also shown.