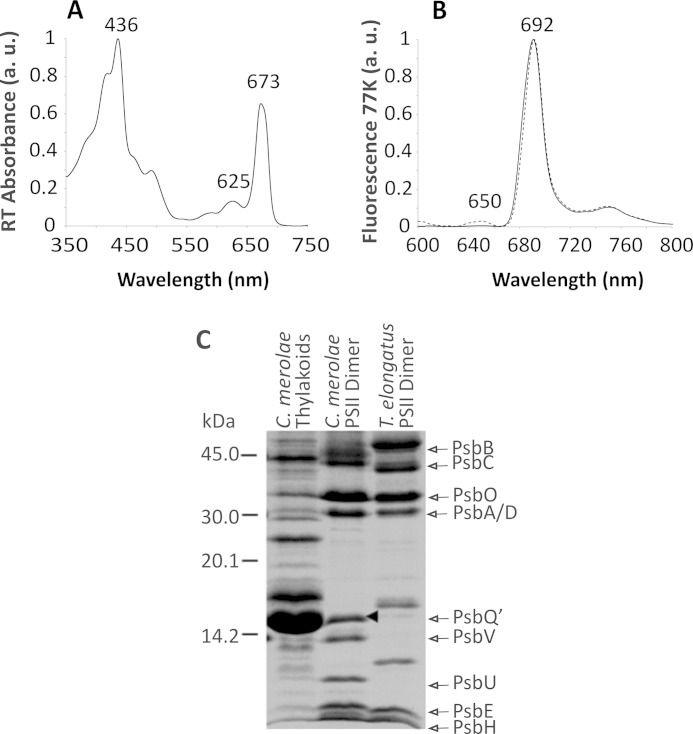
FIGURE 2.
Spectroscopic and compositional analyses of the C. merolae PSII dimer. Room temperature absorbance spectrum of PSII dimer (A) shows the red peak at 673 nm, characteristic of PSII. The PSII complex purity was expressed as a ratio of A673/A625 and was estimated at ∼5, confirming a complete removal of residual phycobilisomes. The 77 K steady-state fluorescence emission spectra (B) were taken at excitation wavelengths of 440 nm (solid line) and 580 nm (dashed line). The excitation wavelength of 580 nm was used to detect any residual contamination with phycobilisomes that emit fluorescence at 625 nm. The 440-nm wavelength excited Chla to produce a symmetric emission peak at 692 nm, characteristic of PSII. C, SDS-PAGE protein profile of the C. merolae PSII dimer. Samples (5 μg of Chl/lane) were resolved on a 18% Tris-Tricine gel. The positions of PsbA/C and PsbB/C as well as PsbO, PsbQ′, PsbV, and PsbU were identified by Western blotting and MS/MS analyses. The position of PsbQ′ is marked with an arrowhead in C. a.u., arbitrary units.