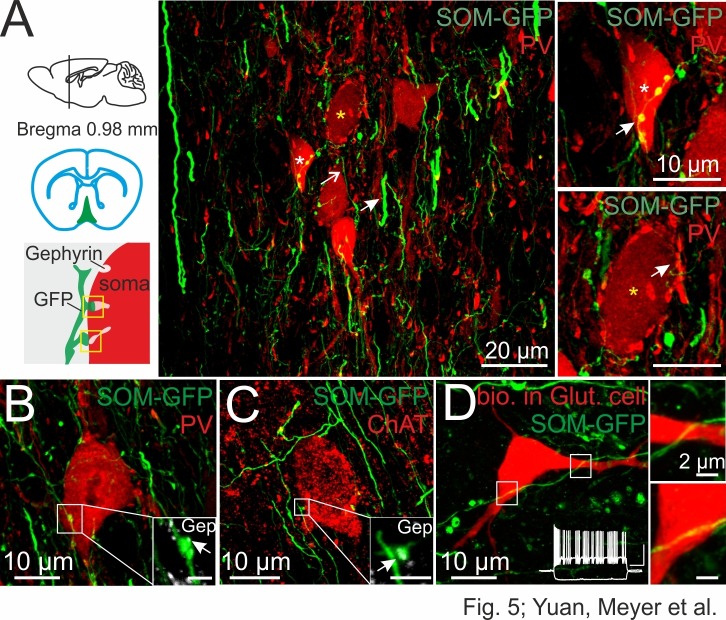
Figure 5. DG-SOMIs form putative synapses onto septal GABAergic, cholinergic and putative glutamatergic cells.
(A) Confocal image stack of SOM fibers expressing GFP in the medial septum and vertical limb of the diagonal band of Broca (MSvDB) upon rAAV-FLEX-GFP injection bilaterally in the dorsal DG of SOM-Cre mice. Thin GFP-positive fibers (open arrow) form ‘en passant’ bouton-like varicosities at close proximity to cell bodies of PVIs (red). Somata marked with a white and yellow star are shown on the right at higher magnification. Top right, arrow points to putative synaptic contacts formed by DG-septal SOMIs. Bottom right, PVI cell bodies are surrounded by PV-expressing boutons very likely originating from local PVIs (arrow). (B,C) Confocal image stacks of putative synaptic contacts formed by DG-septal projecting SOMIs at a PVI soma (B) and at a cell body expressing choline acetyltransferase (ChAT, (C). Insets, high magnifications of the putative contact sites colocalizing gephyrin (Gep; arrow). Scale bar, 2 µm. (D) Intracellularly labeled cell in the MSvDB with biocytin during whole-cell recordings (red). The cell showed a burst-like discharge pattern (inset; cluster-firing cells) during depolarizing current injections (1 s, 300 pA; −100 pA) characteristic for glutamatergic (Glut) neurons in the MSvDB (Manseau et al., 2005; Mattis et al., 2014). White boxes are magnified on the right and show SOMI-GFP fibres in close proximity of the soma and the proximal dendrite of the putative glutamatergic cell. Note, lacking bouton-like shape of this putative contact site.