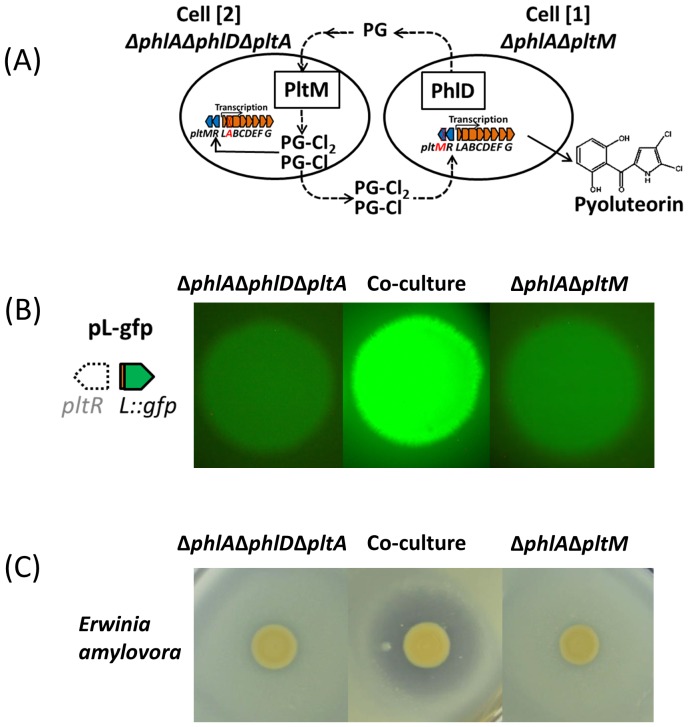
Figure 7. PG-Cl and PG-Cl2 function as cell-cell communication signals of P. protegens Pf-5.
(A) Proposed cell-cell communication model. Cell [1] (ΔphlAΔpltM) produces phloroglucinol (PG) and releases it into the environment. PG is taken up by cell [2] (ΔphlAΔphlDΔpltA) and converted into PG-Cl and PG-Cl2, which are secreted into the environment. PG-Cl and PG-Cl2 are taken up by cell [1] and induce expression of pyoluteorin biosynthetic genes and production of pyoluteorin by cell [1]. The plt gene cluster is shown. Red font indicates that the gene was deleted. (B) GFP expression from the pure- and co-culture of the ΔphlAΔpltM mutant containing pL-gfp and the ΔphlAΔphlDΔpltA mutant containing pL-gfp on NAGly plate. (C) Antibiosis of the pure- and co-culture of the ΔphlAΔpltM mutant and ΔphlAΔphlDΔpltA mutant against growth of Erwinia amylovora on a NAGly plate. The co-culture was prepared by mixing the two mutants 1:1 and spotting on the plate. The experiment was repeated at least twice, with similar results.