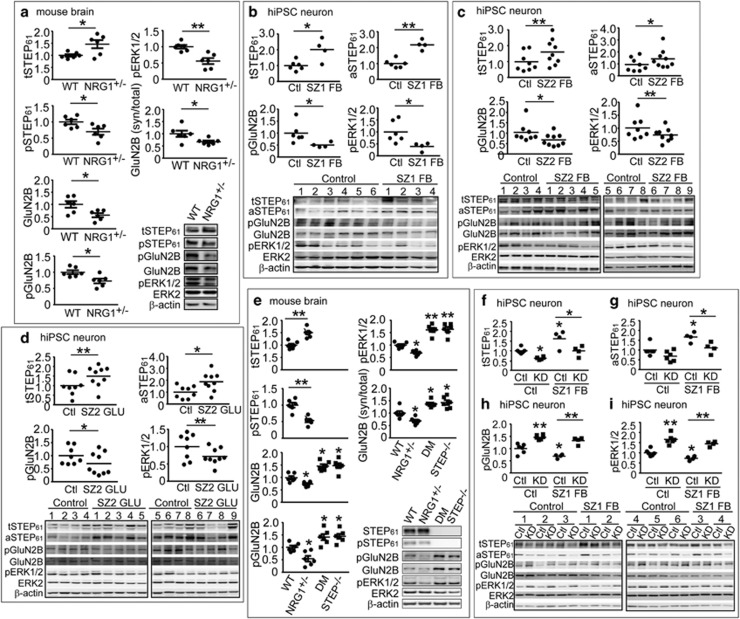
Figure 1.
STEP61 level is elevated in Nrg1+/− mice and human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) neurons from schizophrenia (SZ) patients. (a) STEP61 level is elevated in Nrg1+/− mice. P2 membrane fractions from 9-month-old Nrg1+/− mice were processed by western blotting (WB) using antibodies against total STEP61, phosphorylated STEP61 (pSTEP61, inactive) and tyrosine phosphorylation of STEP substrates GluN2B and ERK1/2. All antibodies are listed in Supplementary Table S4. (b–d) STEP61 level is elevated in SZ hiPSC neurons. Total STEP61 (tSTEP61), active STEP61 (aSTEP61) and Tyr phosphorylation of STEP substrates (GluN2B and ERK1/2) levels were probed in SZ1 forebrain (FB) neurons (b), SZ2-FB hiPSC neurons (c) and SZ2 Ngn2-induced excitatory (GLU) neurons (d). Detailed description of patients and demographic summary can be found in Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Tables S1 and S2 (e) Tyr phosphorylation of STEP substrates is restored in Nrg1+/− mice null for STEP. P2 fractions from wild-type (WT), Nrg1+/−, STEP−/− and Nrg1+/− STEP−/− (double mutant, DM) mice were processed by WB and probed for targets shown in the figure. (f–i) STEP lentiviral (LV) short hairpin RNA knockdown (KD), relative to LV-scrambled control (Ctl), resulted in significantly decreased tSTEP61 (f) and aSTEP61 (g) levels and increased phosphorylation of the STEP61 substrates pGluN2B (h) and pERK1/2 (i) in SZ1-FB hiPSC neurons. Mice data are expressed as mean±s.e.m. and statistical significance was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni’s test (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, n=6 each group). hiPSC neuron data are expressed as mean values from 3 to 6 replicates and statistical significance was determined by nested ANOVA analyses (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, SZ1-FB: 6 controls and 4 patients; SZ2-FB and SZ2-GLU: 8 controls and 9 patients).