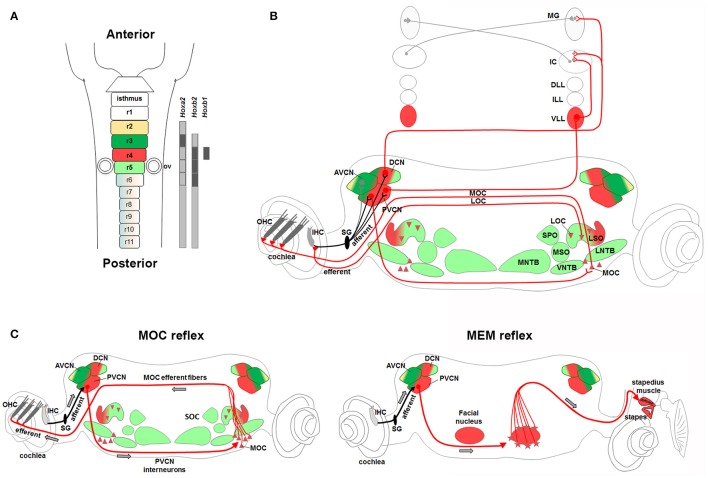
Figure 6.
Rhombomere 4-derived auditory subcircuits. (A) Schema of hindbrain, in which rhombomeres 2–5 are color-coded, and associated Hox genes expression. (B,C) R4-derived subcircuits involved in the transmission of auditory sounds (CN, VLL), protection from acoustic injury (MOC/MEM reflex and LOC), amplification of low-level sounds (MOC innervation to OHC). (C) R4-derived PVCN neurons and motor MOC and FBM neurons contribute to the efferent reflex of MOC and MEM reflex, respectively. Modified from Di Bonito et al. (2013a). Hoxb1 and Hoxb2 act primarily upon assembly of r4-derived structures, contributing to the main pathway of sound transmission, as well as in the establishment of sensorimotor reflex circuits important for cochlea protection and amplification processes.