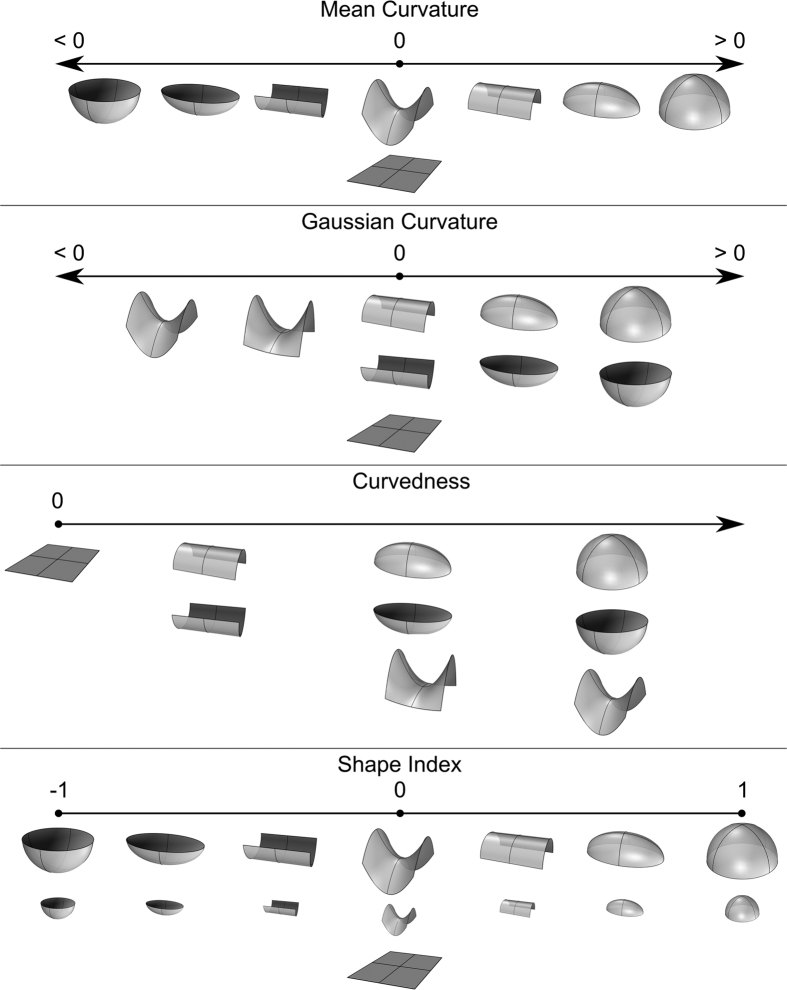
Figure 5. Topological characteristics of curvature indices.
Each descriptor highlights different attributes of the surface’s underlying topology. MC differentiates significantly areas of high and low curvature, as well as convex and concave shapes. GC discriminates well between spherical and saddle-like areas. CU is less representative of a particular morphology and reflects the absolute curvature magnitude in each point, irrespective of its specific shape. Finally, SI is scale-independent and able to differentiate between pure shape characteristics, e.g domes, ridges and saddles, regardless of their high or low CU.