Fig. 1.
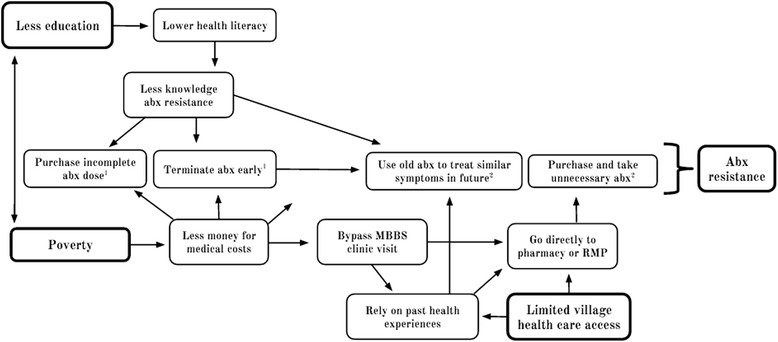
Hypothesized relationships between education, income, healthcare access, and antibiotic resistance. The four central outcomes, purchasing an incomplete antibiotic dose, terminating antibiotics early, using old antibiotics to treat similar symptoms in the future, and purchasing and taking unnecessary antibiotics, were all predicted to be associated with an increase in antibiotic resistance (far right). abx = antibiotics. 1Classified as shortened antibiotic courses; 2Classified as antibiotic overuse
