Fig. 7.
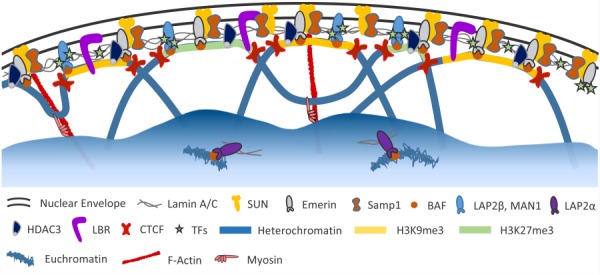
Proteins associated with the nuclear lamina. In addition to the components of the LINC complex, numerous lamina-associated polypeptides (LAPs) bind to the nuclear lamina and serve various functions. Emerin, LAP2β, and MAN1 help connect heterochromatic LADs to the nuclear lamina via their interaction with BAF. In addition, HDAC3 and LBR directly bind chromatin. These proteins, as well as the nuclear lamina itself, also bind various transcription factors (TFs) involved in important signaling pathways (e.g., c-Fos, SREB1, β-catenin, and Smads). CTCF helps position chromatin at the nuclear envelope and also flanks regions of histone modifications associated with gene silencing (i.e., H3K9me3 and H3K27me3). Soluble lamin A/C dimers associate with actively transcribed euchromatin within the nuclear interior via LAP2α. Lamin A/C and emerin are also likely involved in the actomyosin machinery potentially responsible for relocating gene loci to the nuclear interior upon activation. Color figures are available online.
