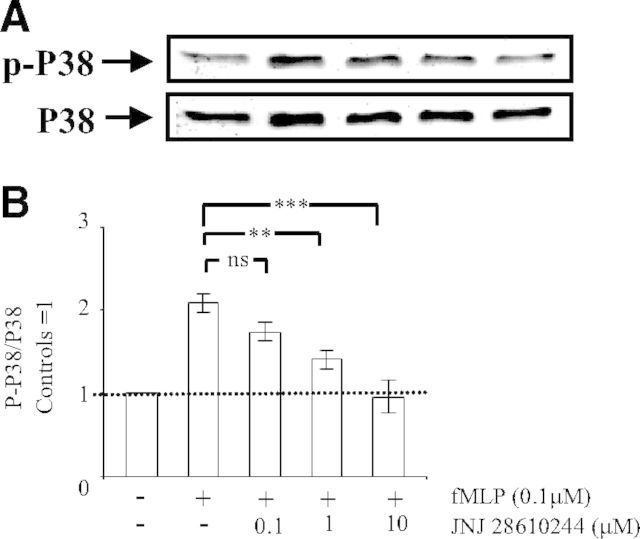
Figure 5. Engagement of the H4 receptor prevents Mac-1-dependent activation of p38 MAPK.
Human PMNs (5×106) were preincubated for 5 min without (−) or with (+) the indicated concentrations of the H4 receptor agonist JNJ 28610244. Thereafter, PMNs were incubated on plates coated with fibrinogen, and fMLP (0.1 μM) was added to engage Mac-1. After 30 min, the cells were lysed. Proteins (40 μg) in lysate extracts were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a PVDF membrane, which was incubated with a mouse anti-p-p38 MAPK antibody, followed by secondary goat anti-rabbit peroxidase-conjugated antibodies. Detection of the signals was carried out by ECL. Membranes were stripped off anti-p-p38 MAPK antibodies, and Western blot analysis was carried out with a rabbit anti-p38 MAPK antibody, followed by secondary goat anti-rabbit peroxidase-conjugated antibodies and ECL detection. (A) Representative Western blot; the arrows indicate the position of p-p38 MAPK and p38 MAPK. (B) Results after densitometric analysis (in arbitrary units) of the p-p38 MAPK/p38 MAPK ratio for each individual blot. The densitometric analysis of the p-p38 MAPK/p38 MAPK ratio is expressed as fold increase over control cells and represents means ± sem of three separate experiments. **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni's test compared with fMLP-stimulated adherent cells.