Fig. 2.
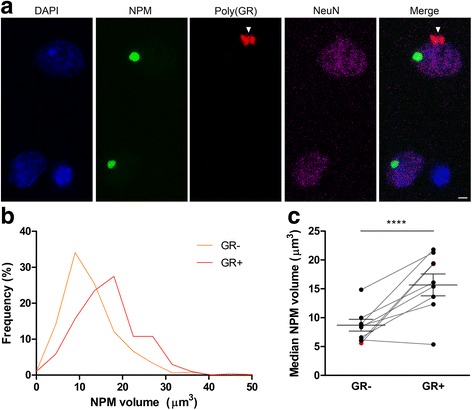
Increased nucleolar volume in poly(GR) inclusion-bearing neurons in C9FTLD patient brain. a Representative images of frontal cortex from a heterozygous C9FTLD case immunostained for the nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (NPM, green), poly(GR) protein (red), the neuronal marker (NeuN, magenta) with DAPI nuclear stain (blue); a typical poly(GR) inclusion is arrowed. Scale bar represents 2 μm. b, c Quantification of neuronal nucleolar volume determined by nucleophosmin immunoreactivity. Frequency distribution of pooled C9FTLD (heterozygous cases only) nucleolar volumes show a shift to increased volumes in neurons bearing poly(GR) inclusions compared with neurons without inclusions (b). Median nucleolar volume in C9FTLD cases was significantly larger in neurons with poly(GR) inclusions (GR+) compared with neurons without inclusions (GR-) (c). Each dot represents an individual case with the homozygous C9FTLD case shown in red, grey lines link medians from the same cases in neurons with or without poly(GR) inclusions, and the average and SEM of heterozygous cases are shown as long and short horizontal bars, respectively. Significance was determined by paired regression analysis: ****p < 0.0001
