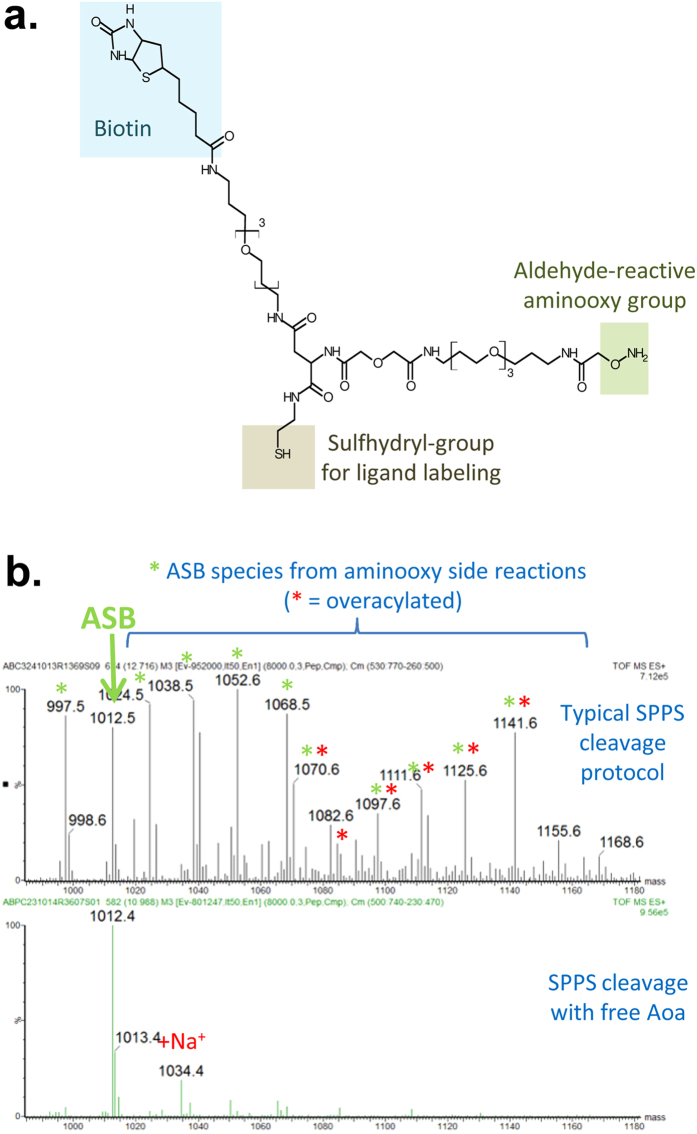
Figure 1. ASB crosslinker design and synthesis.
(a) Chemical structure of ASB crosslinker highlighting its three functional groups. Both biotin and the aminooxy group are separated from the sulfhydryl by PEG-based linkers to provide separation (~33 Å) from the sulfhydryl group, which is used to link ASB to the ligand. (b) Mass spectrum of ASB synthesized using a typical solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) protocol (top panel) and after modifications (bottom panel). The expected monoisotopic m/z for ASB is 1012.5 Da. Typical cleavage protocols resulted in masses that correspond to the addition of aldehyde contaminants to the aminooxy group of ASB (green asterisks) and to overacylation during the final coupling step leading to the addition of two aminooxy groups (red asterisks). Modifications, including addition of free aminooxyacetic acid (Aoa) during the resin cleavage step and use of collidine as the base during the final coupling reaction, greatly decreased these undesirable side products.