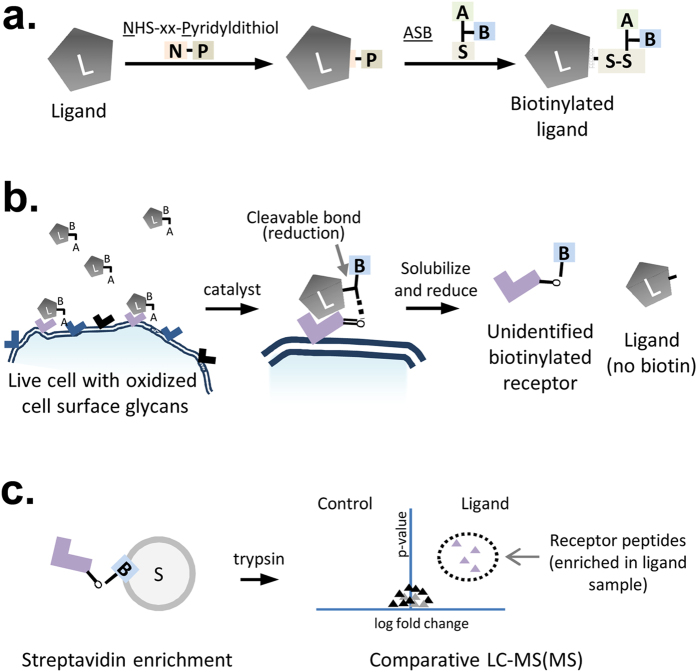
Figure 2. Biotin transfer workflow for identification of the ligand-binding partner.
(a) Ligand labelling: Ligands of interest are labelled in a two-step reaction through addition of a commercial amine-to-sulfhydryl crosslinker (LC-SPDP or PEG4 version) followed by addition of ASB. Both a control ligand and a ligand-of-interest are prepared in parallel. (b) Biotin-transfer to cell surface receptor on periodate-treated live cells: The labelled ligand in incubated with cells to encourage ligand-directed cell surface binding prior to addition of a catalyst to promote oxime bond formation and crosslinking. Cells are then solubilized under reducing conditions resulting in the transfer of the biotin from the ligand to its crosslinked binding partner. (c) Isolation of biotinylated proteins and identification of enriched peptides by comparative mass spectrometry: Biotinylated proteins are immobilized on a streptavidin resin and digested with trypsin. The intensity of peptides resulting from parallel experiments with the control ligand and the ligand-of-interest are then compared using standard mass spectrometry-based proteomic workflows.