Abstract
Background. Portal hypertension, an elevation in the hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG), can be used to monitor disease progression and response to therapy in cirrhosis. Since obtaining HVPG measurements is invasive, reliable noninvasive methods of assessing portal hypertension are needed. Methods. Noninvasive markers of fibrosis, including magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) shear wave velocity, were correlated with histologic fibrosis and HVPG measurements in hepatitis C (HCV) and/or HIV-infected patients with advanced liver disease enrolled in a clinical trial of treatment with simtuzumab, an anti-LOXL2 antibody. Results. This exploratory analysis includes 23 subjects: 9 with HCV monoinfection, 9 with HIV and HCV, and 5 with HIV and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Median Ishak fibrosis score was 4 (range 1–6); 11 subjects (48%) had cirrhosis. Median HVPG was 6 mmHg (range 3–16). Liver stiffness measured by MRE correlated with HVPG (r = 0.64, p = 0.01), histologic fibrosis score (r = 0.71, p = 0.004), noninvasive fibrosis indices, including APRI (r = 0.81, p < 0.001), and soluble LOXL2 (r = 0.82, p = 0.001). On stepwise multivariate regression analysis, MRE was the only variable independently associated with HVPG (R2 = 0.377, p = 0.02). Conclusions. MRE of the liver correlated independently with HVPG. MRE is a valid noninvasive measure of liver disease severity and may prove to be a useful tool for noninvasive portal hypertension assessment. Trial Registration Number. This trial is registered with NCT01707472.
1. Background
Chronic liver injury with progressive hepatic fibrosis can result in cirrhosis, a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide [1]. Portal hypertension, defined as increased pressure within the portal venous system, contributes to the serious complications of end stage liver disease, including gastroesophageal varices and ascites. The established standard for diagnosing portal hypertension is transjugular measurement of the hepatic venous portal gradient (HVPG), the difference between wedged and free hepatic venous pressures. HVPG measurements are utilized in managing liver disease for prognostication, monitoring of progression, and measuring response to therapy [2–5]. However, HVPG measurements are invasive, costly, and often available only at referral centers [6].
Identifying reliable noninvasive markers of portal hypertension would improve clinical ability to determine disease status and monitor fibrosis progression with reduced risk compared with HVPG measurements. A number of laboratory tests and laboratory indices have been evaluated as noninvasive markers of portal hypertension, including platelet count, prothrombin time, and aspartate aminotransferase platelet ratio (APRI); however these markers cannot reliably predict the presence of varices or serve as surrogates for HVPG [7].
Conventional imaging modalities have been used to support a diagnosis of cirrhosis and portal hypertension but have limited utility for confirming the presence of fibrosis or for the longitudinal assessment of portal hypertension [8–10]. Ultrasound-based vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE; Fibroscan) can predict advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis and correlates with HVPG [11]. Liver stiffness measured by VCTE predicts clinical decompensation and complications of portal hypertension [12]. However, VCTE is limited by operator dependence, small sampling window, and unreliability in patients with abdominal obesity or ascites [13].
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is now available as an alternative method for determining liver stiffness. MRE can accurately detect both early and advanced fibrosis [14] and predict the presence of esophageal varices [15]. MRE can be successfully performed in most patients, including those with ascites, anatomical variants, and liver transplant recipients [16]. The accuracy of MRE appears to be superior to VCTE [17, 18], though the number of clinical studies that compare the two methods is small. The use of MRE of the liver in assessment of portal hypertension has been explored in animal models [19]; however studies in humans are limited to the detection of clinical manifestations of portal hypertension, such as the development of esophageal varices [20].
In this prospective, exploratory study, we assessed the accuracy of noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers and MRE shear wave velocity for the diagnosis of fibrosis and portal hypertension in a cohort of hepatitis C (HCV) and/or human immunodeficiency virus- (HIV-) infected liver disease patients. Participants were evaluated as part of a clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of simtuzumab (Gilead Sciences, Inc., Foster City, CA), a humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2), an enzyme that contributes to liver fibrosis by catalyzing collagen cross-linkage.
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population
Adults 18 years of age or older, with HIV, HCV, or HIV/HCV, were enrolled from October 2012 to December 2014. HCV infection was confirmed by measurement of HCV RNA >2,000 IU/mL. For HIV-infected subjects, an HIV viral load <400 copies/mL on stable combination antiretroviral therapy for ≥3 months was required. Patients with known cirrhosis could participate if they were Child-Pugh class A [21].
The NIAID Institutional Review Board approved the study. All participants provided written informed consent (NCT01707472). The primary study results are reported elsewhere [22].
2.2. Transjugular Liver Biopsy with Portal Pressure Measurements
HVPG measurements were obtained during transjugular liver biopsy. The left, middle, and right hepatic veins were cannulated and the free hepatic vein pressure (FHVP) and the wedged hepatic venous pressure (WHVP) were assessed. The WHVP was measured within each hepatic vein branch with gentle inflation of a balloon occlusion catheter. HVPG was calculated by subtracting the FHVP from the WHVP. Peak HVPG is reported and used for analysis.
2.3. Histology
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded liver biopsy sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, Masson's trichrome, or reticulin and interpreted by a single liver pathologist (DEK). Inflammatory activity and fibrosis were scored using the modified histology activity index (Ishak) scoring system [23]. Steatosis was graded on a scale of 0 to 3 based on the percentage of cells with fat according to the NASH-Clinical Research Network scoring system [24]. Stellate cell activation was quantified by immunohistochemical staining for activated smooth muscle actin [25] (Inova Health Systems, Falls Church, VA).
2.4. Magnetic Resonance Elastography
The imaging protocol for magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) has been described previously [26]. Briefly, MR examination was performed on a 3.0T system (Achieva, Philips Medical Systems, Best, Netherlands) using 32-element surface coil. A mechanical transducer set at vibration frequency of 56 Hz was placed against the supine subjects' side at the lowest right rib in the right-left direction. An operator blinded to participant clinical status performed image processing to provide shear wave speed in m/sec.
2.5. Laboratory Markers of Fibrosis
Platelet counts, liver-associated enzymes including alkaline phosphatase, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), and noninvasive estimators of liver fibrosis validated in similar liver disease populations, including the APRI [27], FIB-4 [28], Forns [29], and Fibroindex [30], were determined at the time of liver biopsy.
2.6. Soluble LOXL2
Soluble LOXL2 (sLOXL2) concentrations were measured in serum using a proprietary immunoassay (Singulex, Alameda, CA).
2.7. Hepatic LOXL2 Gene Expression
In a subset of participants (n = 12), total RNA isolated from liver was reverse transcribed using random primers with the High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcriptase Kit (ThermoFischer Scientific, Waltham, MA), as previously described [22, 31]. Gene expression was determined as cycle of threshold (Ct) based on 40 PCR cycles, using expression of GAPDH and GUSB as endogenous controls to determine delta Ct values. GAPDH Ct values were distributed between 23 and 27. Data from 2 samples was excluded from analysis due to inadequate signal strength, defined as a GAPDH Ct value >27. Thus, confirmatory qRT-PCR data are presented from 10 of 12 subjects. Expression reactions using predesigned Taqman assays assembled into custom-designed 96-well plates (ThermoFischer Scientific) were run on an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System, as previously described [31].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Pairwise correlations between biomarkers of interest were evaluated with Spearman's correlation coefficient. For this exploratory analysis, a p value of ≤0.05, without adjustment for multiple comparisons, was considered statistically significant. Simple linear regression was employed to screen for biomarkers associated with HVPG. Biomarkers with a p value ≤0.15 from the simple linear regressions were identified as potential candidates. Backward stepwise multiple regression analysis was performed on HVPG using the candidate biomarkers. Stepwise variable elimination was based on a threshold p value of ≤0.15. Analyses were performed using JMP v.11 (SAS, Cary, NC, USA).
2.9. Data Availability
Datasets analyzed for the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
Twenty-three patients completed the screening evaluation. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the cohort are shown in Table 1. The median age was 57 years (range 45–76 years) and 78% of participants were males. HCV was present in 18 (78%), 9 of whom had HIV coinfection. Sixteen (89%) of the HCV-infected participants were genotype 1. Five (22%) participants had HIV infection and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) [24].
Table 1.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of study subjects (n = 23).
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 54 (45–76) |
| Male, n (%) | 18 (78%) |
| Liver disease etiology, n (%) | |
| HCV | 9 (39%) |
| HCV/HIV | 9 (39%) |
| HIV/NASH | 5 (22%) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 30 (21–46) |
| >30 kg/m2 (obesity), n (%) | 12 (52%) |
| Laboratory studies | |
| Platelets, K/uL | 159 (45–284) |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | 107 (51–210) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), U/L | 56 (22–151) |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), U/L | 77 (30–161) |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.3–2.3) |
| Direct bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.3 (0.1–1.4) |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), U/L | 150 (19–531) |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.1 (3.0–5.5) |
| Prothrombin time (PT), seconds | 14.3 (12.3–16.4) |
| International normalized ratio (INR) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) |
| Hepatitis C characteristics (n = 18) | |
| HCV viral load, log10, IU/mL | 6.9 (4.7–7.8) |
| Hepatitis C genotype, n (%) | |
| 1a | 13 (72) |
| 1b | 3 (17) |
| 2 | 1 (6) |
| 4 | 1 (6) |
| MRE shear wave velocity, m/sec (n = 15) | 2.13 (1.25–3.03) |
| HVPG, mmHg | 6 (3–16) |
| Liver biopsy length, mm | 12 (6–24) |
| <10 mm, n (%) | 6 (26) |
| Liver biopsy scoring | |
| Fibrosis, Ishak (range 0–6) | 4 (1–6) |
| Inflammation, total HAI (range 0–18) | 8 (1–14) |
| Steatosis (range 0–4) | 1 (0–2) |
Median, range presented unless otherwise noted.
Liver biopsy size ranged from 6 to 24 mm, median 12 mm. Six (26%) of samples were <10 mm and therefore considered suboptimal for staging and grading [32].
Median Ishak fibrosis score was 4 (range 1–6) and 11 participants (48%) had cirrhosis, all Child-Pugh class A. Median HVPG was 8 mmHg (range 3–16 mmHg) and HVPG was ≥10 mmHg in 8 (35%) participants.
3.2. Correlates of HVPG
HVPG (n = 23) correlated positively with AST (r = 0.48, p = 0.01) and GGT (r = 0.62, p = 0.001) and negatively correlated with platelets (r = −0.72, p = 0.002). No significant correlation was seen between HVPG and ALT (Table 2).
Table 2.
Correlation coefficients (Spearman ρ) for selected variables∗.
| MRE shear wave velocity | HVPG | Ishak fibrosis score | sLOXL2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRE shear wave velocity (n = 15) | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.82 | |
| HVPG (n = 23) | 0.64 | 0.53 | 0.58 | |
| Liver biopsy (n = 23) | ||||
| Ishak fibrosis score | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.31 | |
| Total HAI inflammation score | 0.64 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.30 |
| % alpha smooth muscle actin (αSMA) | 0.74 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.08 |
| Selected laboratory studies (n = 23) | ||||
| Platelets | −0.70 | −0.72 | −0.47 | −0.57 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | 0.74 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.70 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.24 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) | 0.43 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 0.28 |
| Non-invasive fibrosis indices (n = 23) | ||||
| APRI | 0.81 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.72 |
| FIB-4 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 0.71 |
| Forns' index | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.44 | 0.60 |
| Fibroindex | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.80 |
| Serum soluble LOXL2 (n = 23) | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.31 | |
| Liver LOXL2 (n = 10) | 0.86 a | 0.69 | 0.18 | 0.31 |
MRE: magnetic resonance elastography; HVPG: hepatic venous pressure gradient; HAI: histologic activity index; APRI: AST/platelet ratio index; LOXL2: lysyl oxidase-like 2.
aMRE and liver LOXL2 results available for 8 participants.
∗ p values are indicated as follows: Italics, 0.01–0.05; Underlined, 0.001–<0.01; Bold, <0.001.
While HVPG correlated with liver biopsy fibrosis score (r = 0.52, p = 0.04), HVPG demonstrated a better correlation with Forns' Index (r = 0.76, p < 0.001), Fibroindex (r = 0.75, p = 0.001), and APRI (r = 0.59, p = 0.02). (Table 2).
Stepwise regression analysis, including AST, GGT, platelets, liver biopsy fibrosis score, and MRE, identified MRE as the only biomarker independently associated with HVPG (R2 = 0.377, p = 0.015).
3.3. Correlates of MRE
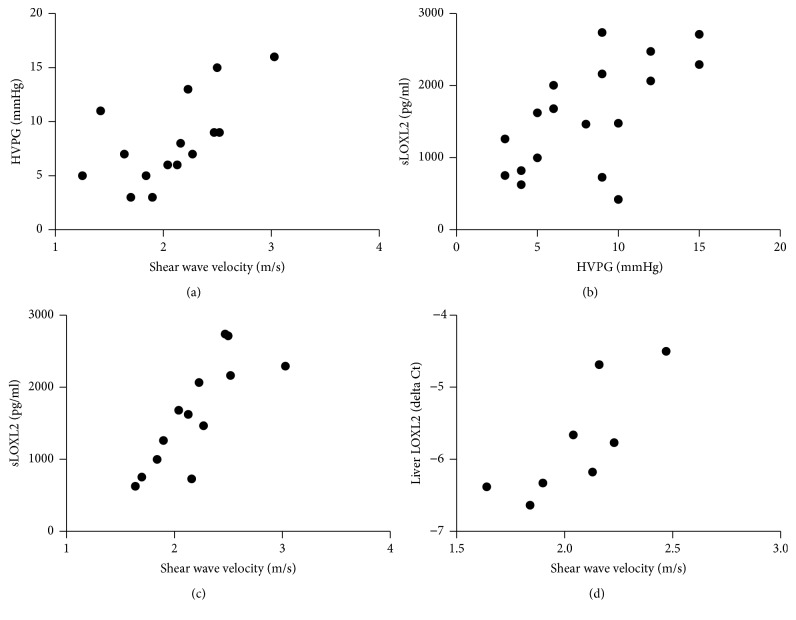
MRE was completed in 15 participants (3 HCV, 7 HIV/HCV, and 5 HIV/NASH). Median shear wave velocity was 2.13 m/sec (range 1.25–3.03 m/sec). MRE correlated significantly with HVPG (r = 0.64, p = 0.009; Figure 1), as well as with Ishak fibrosis score (r = 0.71, p = 0.003), total histologic activity index (HAI) inflammation (r = 0.64, p = 0.01), periportal inflammation (r = 0.72, p = 0.002), lobular inflammation (r = 0.8, p = 0.002), and αSMA (r = 0.70, p = 0.008) (Table 2).
Figure 1.
Significant correlations were seen between MRE-measured shear wave velocity, a measure of liver stiffness, and HVPG (a), sLOXL2 (c), and liver LOXL2 (d). sLOXL2 also correlated well with HVPG (b).
Furthermore, MRE had a significant positive correlation with AST (r = 0.74, p = 0.002) and significant negative correlation with platelets (r = −0.70, p = 0.004). In addition, MRE had significant correlations with noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers, including APRI (r = 0.81, p < 0.001), FIB-4 (r = 0.67, p = 0.006), Fibroindex (r = 0.76, p = 0.001), and Forns' Index (r = 0.72, p = 0.002). No correlation with ALT (r = 0.28, p = 0.31) or GGT (r = 0.43, p = 0.1) was observed.
3.4. Correlates of LOXL2
Soluble LOXL2 (n = 23) levels correlated significantly with AST (r = 0.70, p = 0.001) and negatively with platelets (r = −0.57, p = 0.01) (Table 2). sLOXL2 also had significant positive correlation with the noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers, APRI (r = 0.72, p = 0.001), FIB-4 (r = 0.71, p = 0.001), Fibroindex (r = 0.80, p = <0.0001), and Forns' Index (r = 0.6, p = 0.009).
Soluble LOXL2 correlated with HVPG (r = 0.58, p = 0.02) but did not correlate with fibrosis or inflammation by biopsy.
Liver LOXL2 gene expression, analyzed by PCR in 10 participants, also correlated with HVPG (r = 0.69, p = 0.03) and HAI total (r = 0.82, p = 0.006), but not with fibrosis (r = 0.18, p = 0.61).
Serum soluble (n = 13; r = 0.82, p < 0.001) and liver LOXL2 (n = 8; r = 0.82, p = 0.03) both had strong correlations with MRE (Figure 1).
4. Discussion
We have demonstrated that hepatic MRE measurement of shear wave velocity may be a valuable biomarker in assessing the degree of portal hypertension as measured by HVPG. Stepwise regression analysis of HVPG on multiple biomarkers of interest showed that MRE had an independent association with HVPG, suggesting potential utility of MRE in detection and monitoring of portal hypertension. Additionally, our study demonstrates correlations between MRE-measured hepatic shear wave velocity with other noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers, including APRI, FIB-4, Fibroindex, and Forns' Index, and with sLOXL2 levels, although none of these markers showed an independent association with HVPG in a multivariate analysis.
In porcine and canine models of progressive portal hypertension, liver and spleen stiffness assessed by MRE correlated with portal pressure [19, 33]. In a small human study, MRE was sensitive to pressure when change in volumetric strain was found after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement [34]. This study demonstrated that percentage change in volumetric strain measurements before and after TIPS procedure correlated well with pre-TIPS HVPG. These findings suggest that MRE measures dynamic, pressure-dependent liver stiffness in addition to the static components of fibrosis. However, to the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to identify a strong correlation between MRE-measured shear wave velocity, HVPG, and serum soluble LOXL2. This was possible at higher magnetic field strength (3 T) not used in the previously mentioned studies. A higher magnetic field is known to be more sensitive to phase changes that are the backbone of the MRE readout sequences. Additionally, utilizing 32-channel coils and mechanical vibrations (instead of acoustic vibrations) might have added to the robustness and sensitivity of our methods.
MRE shear wave velocity also correlated with hepatic fibrosis, confirming the findings of earlier MRE studies in HCV and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [35–37]. Interestingly, MRE had a strong correlation with histologic inflammatory scores and αSMA in addition to histologic fibrosis, suggesting that MRE-measured shear wave velocity may detect hepatic inflammation. Studies have shown hepatic inflammation can increase liver stiffness irrespective of fibrosis [38], although the mechanism is not fully understood. However, the increase in cellular volume seen with inflammation may affect the procession of the shear wave as it propagates through the hepatic tissue. The dynamic component of liver stiffness is affected by change in perfusion that can be influenced by hepatic inflammation. Moreover, changes in the mechanical state of cells capable of contraction, such as vascular smooth muscle cells and activated hepatic stellate cells in the perisinusoidal spaces, can influence liver stiffness [39].
A correlation was also seen between αSMA, a contractile protein expressed by activated hepatic stellate cells with the myofibroblast phenotype, and HVPG. αSMA is increased in the liver of patients with chronic liver diseases and correlates with the extent of hepatic fibrosis [40]. In chronic viral hepatitis, αSMA also correlates with necroinflammatory grade, suggesting that hepatocyte necroinflammation drives hepatic stellate cell activation and subsequent fibrogenesis [41]. Our observations agree with accumulating evidence suggesting that stellate cells also regulate liver microcirculation and portal pressure. In animal models of fibrosis, αSMA causes cellular contractility through calcium dependent and independent contractile forces, leading to increased portal resistance [42]. As fibrosis advances, myofibroblasts are recruited and impede portal circulation through vasoactive mediators and interactions with the extracellular matrix [43, 44]. Inhibition of αSMA with nitric oxide in rat and human hepatic stellate cells reduces portal pressure by 20% [45].
We also observed a correlation between sLOXL2 levels, hepatic LOXL2 expression, and portal pressure. In addition to cross-linking collagen, LOXL2 increases matrix tension, triggering fibroblasts to covert to contractile myofibroblasts through activation of hepatic TGFβ1 [46, 47]. LOXL2 also stimulates expression of myofibroblasts grown on collagen matrices through integrin mediated focal adhesion kinase activation [48]. As myofibroblasts regulate portal resistance, LOXL2 may also contribute to development of portal hypertension. Interestingly, sLOXL2 had the most significant correlation with MRE compared to other parameters. Longitudinal studies of hepatic fibrosis, including ongoing trials of simtuzumab in NASH and advanced liver fibrosis, will contribute to the understanding of the function of LOXL2 in fibrosis progression and portal hypertension.
Limitations of our study include the cross-sectional design, small size with limited numbers of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension, and lack of a validation cohort. Further cross-sectional and longitudinal study in a larger population of patients with clinically significant portal hypertension is needed to confirm our findings. Multiple comparisons were made and, though statistically significant, many correlations were weak. Additionally, the liver biopsy samples obtained by transjugular biopsy were small, with 6 (26%) suboptimal for grading, likely resulting in understaging and undergrading of fibrosis [32] and potentially attenuating relationships between biopsy parameters and noninvasive markers. MRE requires specialized hardware, usually only available at academic medical centers, and is limited to patients eligible and tolerant of MR imaging. Compared to transient elastography and other ultrasound-based shear wave elastography methods, MRE would be expected to cost more.
In conclusion, MRE shear wave velocity correlates with noninvasive biomarkers and was independently associated with HVPG. Given this, MRE may prove to be a useful noninvasive measure of disease severity and portal hypertension. In addition, our study demonstrated the novel correlation of soluble LOXL2 and hepatic LOXL2 expression with portal hypertension.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Zachary Goodman, who performed alpha smooth muscle actin staining for the study, the volunteers who participated in this research, and NIH care providers and support staff. This work was supported by the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) Intramural Research Program, NIH Clinical Center, NIAID, and NIDDK and, in part, by an NIH Bench to Bedside Award funded by the Office of AIDS Research and funded in part with federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, under contract HHSN261200800001E.
Abbreviations
- αSMA:
Alpha smooth muscle actin
- ALT:
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
Aspartate aminotransferase
- APRI:
Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index
- FHVP:
Free hepatic vein pressure
- GGT:
Gamma-glutamyl transferase
- HAI:
Histologic activity index
- HCV:
Hepatitis C virus
- HIV:
Human immunodeficiency virus
- HVPG:
Hepatic venous pressure gradient
- LOXL2:
Lysyl oxidase-like 2
- MRE:
Magnetic resonance elastography
- NASH:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- qRT:
Quantitative real time
- RNA:
Ribonucleic acid
- TGFβ1:
Transforming growth factor beta-1
- TIPS:
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
- WHVP:
Wedged hepatic venous pressure
- VCTE:
Vibration-controlled transient elastography.
Disclosure
This paper was presented in part at The Liver Meeting (AASLD), Boston, MA, November 7–11, 2014, and Digestive Disease Week (DDW), Washington, DC, May 16–19, 2015.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Meissner receives grant support from Gilead Sciences, Inc. Drs. Myers and Subramanian are employed by and own stock in Gilead Sciences Inc. All other coauthors report no conflicts of interest.
Authors' Contributions
Ahmed M. Gharib and Ma Ai Thanda Han equally contributed to this work. Ahmed M. Gharib, Eric G. Meissner, David E. Kleiner, Robert P. Myers, G. Mani Subramanian, Shyam Kottilil, Theo Heller, Joseph A. Kovacs, and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for study concept and design; Ahmed M. Gharib, Eric G. Meissner, Mary McLaughlin, Lindsay Matthews, Khaled Z. Abd-Elmoniem, Elliot Levy, Christopher Koh, Theo Heller, Joseph A. Kovacs, and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for acquisition of data; Ahmed M. Gharib, Ma Ai Thanda Han, Eric G. Meissner, David E. Kleiner, Xiongce Zhao, Bisharah Rizvi, Elliot Levy, Christopher Koh, Robert P. Myers, G. Mani Subramanian, Theo Heller, Joseph A. Kovacs, and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for analysis and interpretation of data; Ahmed M. Gharib, Ma Ai Thanda Han, Eric G. Meissner, Joseph A. Kovacs, and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for drafting of the manuscript; David E. Kleiner, Ralph Sinkus, Christopher Koh, G. Mani Subramanian, Theo Heller, Joseph A. Kovacs, and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for critical revision of the manuscript for content; Xiongce Zhao was responsible for statistical analysis; Eric G. Meissner, Shyam Kottilil, and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for obtained funding; Mary McLaughlin, Lindsay Matthews, and Khaled Z. Abd-Elmoniem were responsible for technical or material support; Joseph A. Kovacs and Caryn G. Morse were responsible for study supervision.
References
- 1.Lozano R., Naghavi M., Foreman K., et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–2128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ripoll C., Bañares R., Rincón D., et al. Influence of hepatic venous pressure gradient on the prediction of survival of patients with cirrhosis in the MELD era. Hepatology. 2005;42(4):793–801. doi: 10.1002/hep.20871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Turnes J., Garcia-Pagan J. C., Abraldes J. G., Hernandez-Guerra M., Dell'Era A., Bosch J. Pharmacological reduction of portal pressure and long-term risk of first variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006;101(3):506–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zipprich A., Garcia-Tsao G., Rogowski S., Fleig W. E., Seufferlein T., Dollinger M. M. Prognostic indicators of survival in patients with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Liver International. 2012;32(9):1407–1414. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Groszmann R. J., Garcia-Tsao G., Bosch J., et al. Beta-blockers to prevent gastroesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;353(21):2254–2261. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa044456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bosch J., Abraldes J. G., Berzigotti A., García-Pagan J. C. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2009;6(10):573–582. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Deng H., Qi X., Guo X. Diagnostic accuracy of APRI, AAR, FIB-4, FI, king, lok, forns, and fibroindex scores in predicting the presence of esophageal varices in liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2015;94(42) doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000001795.e1795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Choi Y. J., Baik S. K., Park D. H., et al. Comparison of Doppler ultrasonography and the hepatic venous pressure gradient in assessing portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2003;18(4):424–429. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.02992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim Y. J., Raman S. S., Yu N. C., To'o K. J., Jutabha R., Lu D. S. K. Esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients: evaluation with liver CT. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2007;188(1):139–144. doi: 10.2214/ajr.05.1737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Annet L., Materne R., Danse E., Jamart J., Horsmans Y., Van Beers B. E. Hepatic flow parameters measured with MR imaging and doppler US: correlations with degree of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Radiology. 2003;229(2):409–414. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2292021128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bureau C., Metivier S., Peron J. M., et al. Transient elastography accurately predicts presence of significant portal hypertension in patients with chronic liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2008;27(12):1261–1268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Robic M. A., Procopet B., Métivier S., et al. Liver stiffness accurately predicts portal hypertension related complications in patients with chronic liver disease: a prospective study. Journal of Hepatology. 2011;55(5):1017–1024. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Castéra L., Foucher J., Bernard P.-H., et al. Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: a 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology. 2010;51(3):828–835. doi: 10.1002/hep.23425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yin M., Glaser K. J., Talwalkar J. A., Chen J., Manduca A., Ehman R. L. Hepatic MR elastography: clinical performance in a series of 1377 consecutive examinations1. Radiology. 2016;278(1):114–124. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015142141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shin S. U., Lee J.-M., Yu M. H., et al. Prediction of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis: usefulness of three-dimensional MR elastography with echo-planar imaging technique. Radiology. 2014;272(1):143–153. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14130916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Singh S., Venkatesh S. K., Keaveny A., et al. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance elastography in liver transplant recipients: a pooled analysis. Annals of Hepatology. 2016;15(3):363–376. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1198808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huwart L., Sempoux C., Vicaut E., et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(1):32–40. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ichikawa S., Motosugi U., Morisaka H., et al. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracies of magnetic resonance elastography and transient elastography for hepatic fibrosis. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2015;33(1):26–30. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2014.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yin M., Kolipaka A., Woodrum D. A., et al. Hepatic and splenic stiffness augmentation assessed with MR elastography in an in vivo porcine portal hypertension model. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2013;38(4):809–815. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ronot M., Lambert S., Elkrief L., et al. Assessment of portal hypertension and high-risk oesophageal varices with liver and spleen three-dimensional multifrequency MR elastography in liver cirrhosis. European Radiology. 2014;24(6):1394–1402. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3124-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cholongitas E., Papatheodoridis G. V., Vangeli M., Terreni N., Patch D., Burroughs A. K. Systematic review: the model for end-stage liver disease—should it replace Child-Pugh's classification for assessing prognosis in cirrhosis? Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2005;22(11-12):1079–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Meissner E. G., McLaughlin M., Matthews L., et al. Simtuzumab treatment of advanced liver fibrosis in HIV and HCV-infected adults: results of a 6-month open-label safety trial. Liver International. 2016;36(12):1783–1792. doi: 10.1111/liv.13177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ishak K., Baptista A., Bianchi L., et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology. 1995;22(6):696–699. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kleiner D. E., Brunt E. M., Van Natta M., et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41(6):1313–1321. doi: 10.1002/hep.20701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kweon Y.-O., Goodman Z. D., Dienstag J. L., et al. Decreasing fibrogenesis: an immunohistochemical study of paired liver biopsies following lamivudine therapy for chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Hepatology. 2001;35(6):749–755. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Herzka D. A., Kotys M. S., Sinkus R., Pettigrew R. I., Gharib A. M. Magnetic resonance elastography in the liver at 3 Tesla using a second harmonic approach. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2009;62(2):284–291. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wai C.-T., Greenson J. K., Fontana R. J., et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38(2):518–526. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sterling R. K., Lissen E., Clumeck N., et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology. 2006;43(6):1317–1325. doi: 10.1002/hep.21178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Forns X., Ampurdanès S., Llovet J. M., et al. Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model. Hepatology. 2002;36(4, part 1):986–992. doi: 10.1016/s0270-9139(02)00107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Koda M., Matunaga Y., Kawakami M., Kishimoto Y., Suou T., Murawaki Y. Fibroindex, a practical index for predicting significant fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2007;45(2):297–306. doi: 10.1002/hep.21520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Meissner E. G., Wu D., Osinusi A., et al. Endogenous intrahepatic IFNs and association with IFN-free HCV treatment outcome. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2014;124(8):3352–3363. doi: 10.1172/jci75938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rockey D. C., Caldwell S. H., Goodman Z. D., Nelson R. C., Smith A. D., American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Liver biopsy. Hepatology. 2009;49(3):1017–1044. doi: 10.1002/hep.22742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nedredal G. I., Yin M., McKenzie T., et al. Portal hypertension correlates with splenic stiffness as measured with MR elastography. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2011;34(1):79–87. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hirsch S., Guo J., Reiter R., et al. Towards compression-sensitive magnetic resonance elastography of the liver: sensitivity of harmonic volumetric strain to portal hypertension. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2014;39(2):298–306. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Loomba R., Wolfson T., Ang B., et al. Magnetic resonance elastography predicts advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study. Hepatology. 2014;60(6):1920–1928. doi: 10.1002/hep.27362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huwart L., Sempoux C., Salameh N., et al. Liver fibrosis: Noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology. 2007;245(2):458–466. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2452061673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Loomba R., Cui J., Wolfson T., et al. Novel 3D magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in NAFLD: a prospective study. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2016;111(7):986–994. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Arena U., Vizzutti F., Corti G., et al. Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology. 2008;47(2):380–384. doi: 10.1002/hep.22007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tomasek J. J., Gabbiani G., Hinz B., Chaponnier C., Brown R. A. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2002;3(5):349–363. doi: 10.1038/nrm809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Carpino G., Morini S., Ginanni Corradini S., et al. Alpha-SMA expression in hepatic stellate cells and quantitative analysis of hepatic fibrosis in cirrhosis and in recurrent chronic hepatitis after liver transplantation. Digestive and Liver Disease. 2005;37(5):349–356. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2004.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chu C.-M., Shyu W.-C., Liaw Y.-F. Comparative studies on expression of α-smooth muscle actin in hepatic stellate cells in chronic hepatitis B and C. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2008;53(5):1364–1369. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9997-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Laleman W., Van Landeghem L., Severi T., et al. Both Ca2+-dependent and -independent pathways are involved in rat hepatic stellate cell contraction and intrahepatic hyperresponsiveness to methoxamine. American Journal of Physiology—Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2007;292(2):G556–G564. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00196.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Melton A. C., Datta A., Yee H. F., Jr. [Ca2+]i-independent contractile force generation by rat hepatic stellate cells in response to endothelin-1. American Journal of Physiology—Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2006;290(1):G7–G13. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00337.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Novo E., Cannito S., Morello E., et al. Hepatic myofibroblasts and fibrogenic progression of chronic liver diseases. Histology and Histopathology. 2015;30(9):1011–1032. doi: 10.4670/HH-11-623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Duong H. T. T., Dong Z. X., Su L., et al. The use of nanoparticles to deliver nitric oxide to hepatic stellate cells for treating liver fibrosis and portal hypertension. Small. 2015;11(19):2291–2304. doi: 10.1002/smll.201402870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Barry-Hamilton V., Spangler R., Marshall D., et al. Allosteric inhibition of lysyl oxidase-like-2 impedes the development of a pathologic microenvironment. Nature Medicine. 2010;16(9):1009–1017. doi: 10.1038/nm.2208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wipff P.-J., Rifkin D. B., Meister J.-J., Hinz B. Myofibroblast contraction activates latent TGF-β1 from the extracellular matrix. Journal of Cell Biology. 2007;179(6):1311–1323. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200704042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Barker H. E., Bird D., Lang G., Erler J. T. Tumor-secreted LOXL2 activates fibroblasts through FAK signaling. Molecular Cancer Research. 2013;11(11):1425–1436. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-13-0033-t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]