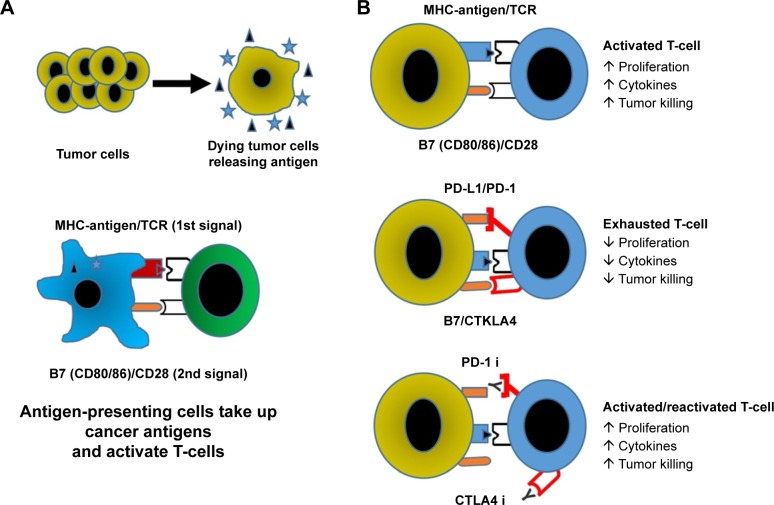
Figure 1.
Immune response to tumors.
Notes: (A) Dying tumor cells are taken up by antigen-presenting cells (eg, dendritic cells) and presented to T-cells (commonly in the lymph system) where they then undergo clonal expansion and trafficking into the tumor. (B) Activated cytotoxic T-cells proliferate, participate in generation of inflammatory and toxic cytokines, including fatal secretion of perforin and granzyme; following chronic stimulation checkpoint receptors on the T-cells are bound by their ligands and the T-cell response is terminated. Blocking the PD-1 and/or CTLA4 checkpoints with antibodies leads to activation/reactivation of T-cells so they generate an antitumor response.
Abbreviations: MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1.