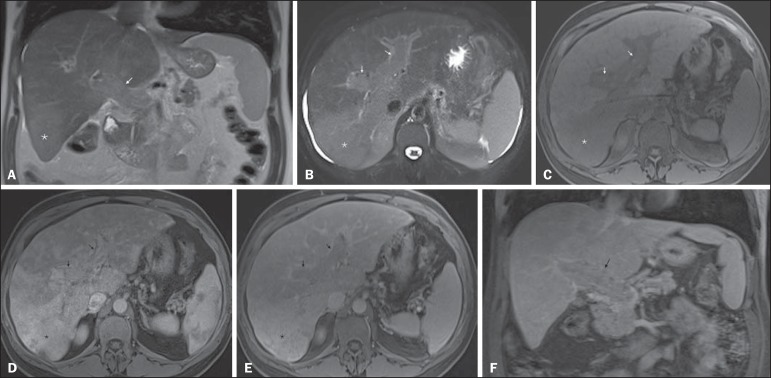
Figure 7.
Diffuse HCC in a patient with chronic hepatitis C. Coronal SS-FSE T2-WI (A), axial fat-suppressed SS-FSE T2-WI (B), axial pre- (C) and postcontrast fat-suppressed 3D-GRE T1-WI in the arterial (D) and interstitial (E) phases, and coronal postcontrast fat-suppressed 3D-GRE T1-WI in the interstitial phase (F). A diffuse area of mild high-signal intensity on T2-WI (asterisk, A,B) is depicted on the right liver lobe, showing low-signal intensity on pre-contrast T1-WI (C). On the dynamic postcontrast images, the lesion is hypervascular at the arterial phase (D) and shows delayed heterogeneous mottled washout (E,F). These features are diagnostic of diffuse HCC. Note the tumor thrombus filling and expanding the portal vein, typical of this type of HCC (arrows, A–F). The thrombus shows hypervascular characteristics and delayed washout comparable to the MRI dynamic features of the tumor.