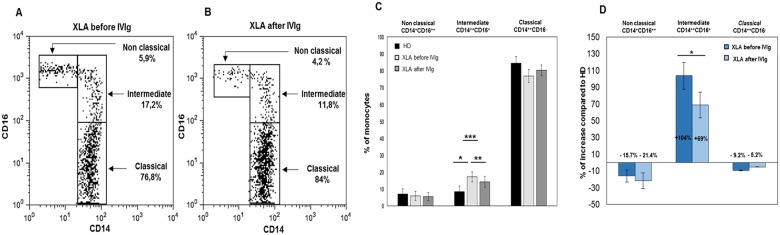
Fig 1. Frequencies of non classical, intermediate and classical monocytes increased from XLA patients before and after IVIg infusion respect to HD.
(A and B) Monocytes subpopulations were phenotypically classified according to their expression of CD14 and CD16 into classical (CD14++CD16-), intermediate (CD14++CD16+) and non classical monocytes (CD14+CD16++) in a representative XLA patient before and after IVIg infusion. Percentages denote mean values. (C) Histograms show that non classical and classical monocyte frequencies from XLA patients are similar to that observed on HD and that IVIg infusion did not change their frequency. Intermediate monocytes percentage is increased in XLA patients (▪p = 0.01), IVIg infusion induce their reduction (▪▪p = 0.04) even if remained at higher level respect to HD (▪▪▪p = 0.01). (D) Histograms denote the percentage of increase of the three monocytes subsets of XLA patients respect to HD. Histograms denote mean values and bars standard deviation. Statistical significance as determined by the nonparametric Mann Whitney and Wilcoxon Signed Rank test is indicated as p value.