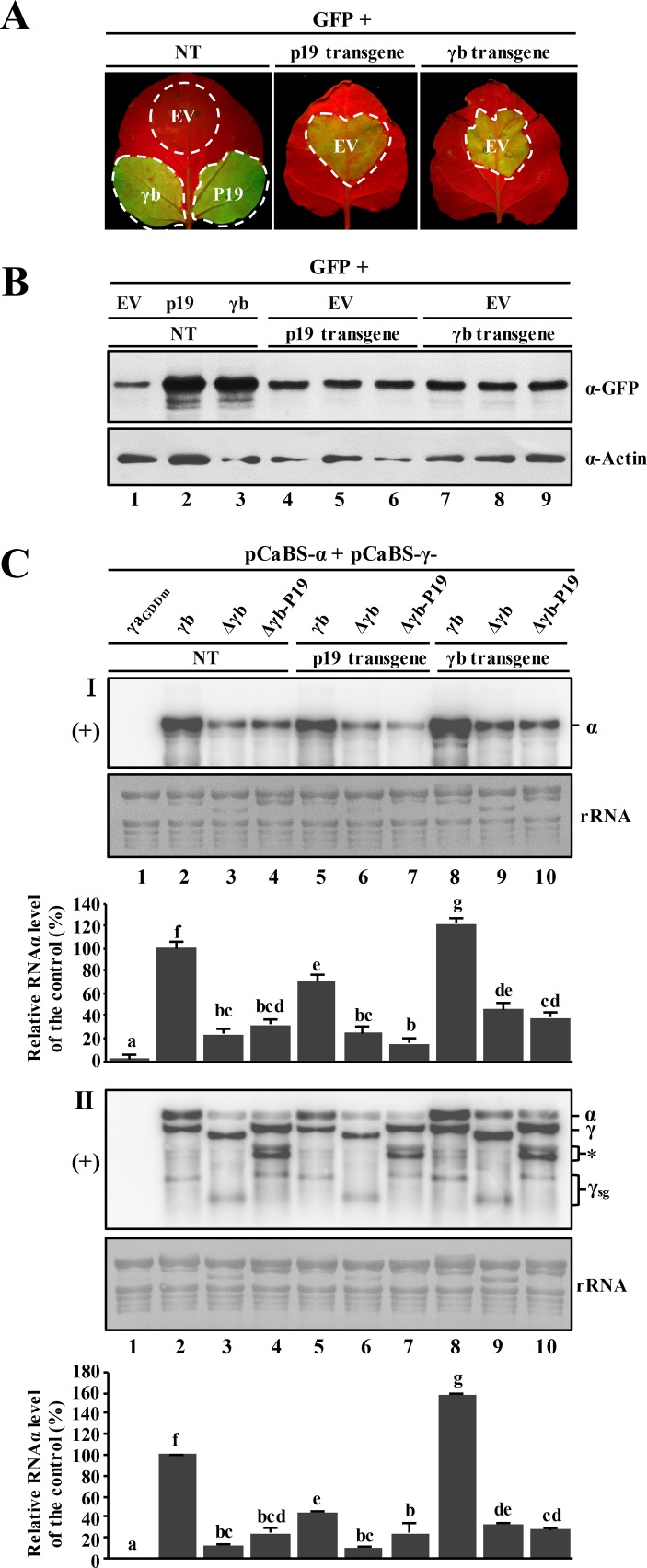
Fig 6. Inability of the p19 VSR protein to restore RNAα accumulation in leaves infected with γb-deficient BSMV mutants.
Panel A: Spot silencing assays comparing RNA silencing suppression abilities of transgenic N. benthamiana expressing p19 or γb versus non-transgenic N. benthamiana. The plants were co-infiltrated with the 35S-GFP vector plus the pGD empty vector (EV), and observed at 3 dpi under UV illumination for GFP fluorescence. Transient expression of γb in non-transgenic plants served as positive controls. Panel B: Western blot analysis of GFP expression in agro-infiltrated regions of the N. benthamiana leaves shown in Fig 6A. Sample loading was determined by total Actin immunoblots. Panel C: Northern blot analysis of viral plus-strand (+) RNA accumulation in γb-deficient BSMV infected leaves with RNAα- (panel I) and 3′-UTR-specific (panel II) probes, respectively. The p19 or γb expressing transgenic plants or non-transgenic plant leaves were agroinfiltrated with the RNAα + RNAγ-derivatives as shown above the panel lanes. The γa replicase was inactivated by mutating the GDD motif to GAD (γaGDDm) in order to prevent BSMV replication. RNAα + RNAγγaGDDm served as a negative control (lane 1). Information about the plasmids used for infiltration is shown in S2C Fig. RNAα, RNAγ and sgRNAγ bands are indicated on the right. Note: the doublets migrating between RNAγ and γsg (panel II, asterisk) have an unknown origin and were observed in previous studies [92]. Methylene blue stained rRNAs were used as a loading control. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. Comparisons of RNAα levels were shown below the corresponding rRNA loading panel. The bar graphs below the RNA blots show the means of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard error (n = 3). In each bar chart, different letters above the bars denote statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) determined by the Duncan's multiple range test.