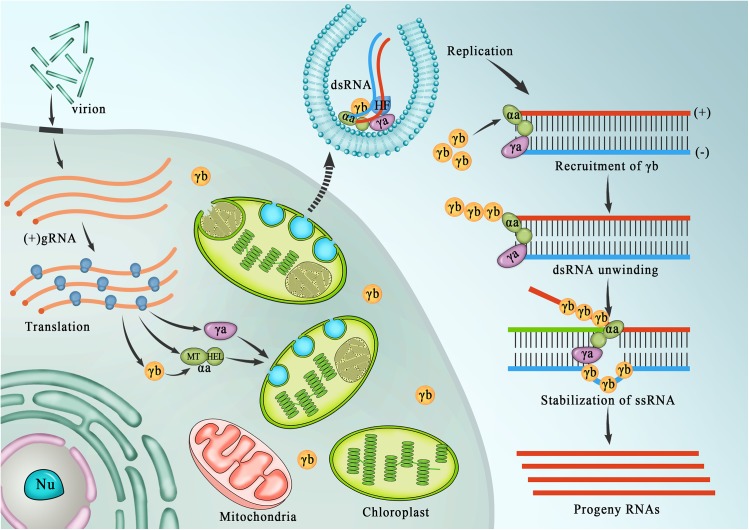
Fig 8. Model outlining the roles of γb in BSMV replication.
Model emphasizing γb activities during the BSMV RNA replication cycle. During initial stages of replication, the αa and γa subunits are translated from the genomic (g) RNAs and form heterologous associations with putative host factors (HF) needed for assembly of the viral replication complex (VRC). The αa replicase subunit interacts with the γa replicase, and facilitates chloroplast localization. After assembly of replication competent VRCs, the viral replicase uses the parental gRNA as a template for synthesis of minus-strand gRNA, and the two strands interact closely to form a dsRNA replication template. During early stages of replication, the dsRNA may function as a template for synthesis of plus-strand progeny RNAs that initially function in translation of the αa and γa replicase subunits. Subsequently, synthesis of sgRNAs is initiated from the minus-strand template, and the γb proteins are translated and recruited to chloroplasts by αa. The γb proteins then bind to the αa subunit where enhance αa helicase activities to stimulate asymmetric synthesis of progeny plus-strand RNAs from the minus-strand templates.